Ever found yourself in front of a class, wondering why, despite their best efforts, some students just can’t seem to get the gist of what they’re reading? It’s a common puzzle for educators everywhere, highlighting the need to understand how to improve reading comprehension effectively.
Math & ELA | PreK To Grade 5
Kids see fun.
You see real learning outcomes.
Watch your kids fall in love with math & reading through our scientifically designed curriculum.
Parents, try for free Teachers, use for free
This blog is your go-to resource, packed with easy-to-implement strategies to boost kids’ reading comprehension. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a comprehensive toolkit to help your students become more proficient and confident readers.
16 Strategies to Improve Reading Comprehension Skills
Improving reading comprehension is essential for a student’s academic success. Here, we explore effective strategies that can make a significant difference:
1. Previewing Texts
Before diving into a text, encourage your students to take a moment to preview it. This means looking at the title, headings, pictures, or graphs. For example, if the text is about the water cycle, ask them to predict what they might learn by examining these features. This strategy is a cornerstone of how to improve reading comprehension as it sets the stage for understanding the content ahead.
2. Making Connections
Helping students connect the text with their experiences, other texts, or the world enhances their engagement and understanding. For instance, if they’re reading a story set in a different country, discuss how the setting or culture compares to theirs. This approach is fundamental in how to help with reading comprehension, making the material more relatable and easier to grasp.
3. Questioning
Fostering an environment where students feel comfortable asking and answering questions about the text is crucial. As they read, prompt them with questions like, “Why do you think the character did that?” This not only keeps them engaged but also deepens their understanding. Incorporating this among your reading comprehension tips encourages active reading and critical thinking.
Begin here
4. Visualizing
Encourage your students to create mental images of what they are reading. For example, if the text describes a dense forest, have them imagine the sights, sounds, and smells. This visualization technique is a powerful reading strategy to improve comprehension, making abstract or complex ideas more concrete and memorable.
Begin here
5. Inferring
Inferring involves reading between the lines to understand the meaning that isn’t explicitly stated. It’s a critical skill for reading comprehension, requiring students to use their prior knowledge and clues from the text to draw conclusions. For example, if a character slams a door and storms out in a huff, students might infer that the character is angry, even if the text doesn’t directly say so. Teaching students to look for emotional cues or descriptive details helps them grasp deeper meanings and nuances in the text.
Begin here
6. Summarizing
Summarizing is a key component of reading strategies to improve comprehension. It involves condensing a text to its main points and key details, enabling students to distill essential information and improve their recall. For instance, after reading a story, ask students to write a few sentences summarizing the plot, focusing on the main events and the conclusion. This practice helps them to identify what’s important in a text and to remember it better.
Begin here
7. Analyzing Text Structure
Understanding how a text is organized is crucial in how to improve comprehension skills. Different texts have different structures, such as chronological order, cause and effect, or problem and solution. Teaching students to recognize these structures helps them predict and understand the information presented. For example, in a science text discussing pollination, the cause-and-effect structure helps students link the role of bees to the success of plant reproduction. Recognizing these structures aids in navigating the text more effectively.
Begin here
8. Vocabulary Development
Expanding students’ vocabulary is fundamental to improving comprehension skills. A rich vocabulary allows students to understand more complex texts with less effort. Incorporate vocabulary lessons into reading sessions by highlighting new words, using them in sentences, and discussing their meanings in context. For instance, if a book mentions “camouflage,” discuss its meaning, show pictures, and use the word in various sentences. This contextual learning makes new words stick and enhances comprehension.
9. Using Graphic Organizers
Graphic organizers are visual tools that help students organize information and ideas from a text. Whether it’s a Venn diagram for comparing and contrasting two characters or a story map to outline the plot, these organizers make abstract ideas tangible. Students can better understand and retain the material by visually mapping out the elements of a text. For example, after reading a chapter, have students fill out a story map to highlight the setting, main characters, problem, and solution, reinforcing their understanding of the story’s structure.
10. Guided Reading
If you are looking for a more personalized approach, guided reading can be just right for you. In small groups, students read texts at their appropriate level, with the teacher providing targeted instruction and support. This might involve pre-reading discussions to activate prior knowledge, shared reading to model fluency and expression, and post-reading questions to assess comprehension. For example, in a guided reading session, a teacher might focus on sequencing by asking students to order events from the story they just read. This individualized attention allows for immediate feedback and addresses specific comprehension challenges.
Begin here
11. Teaching Chronological Understanding
Understanding the sequence of events in a text is a crucial part of how to get better at reading comprehension. This involves recognizing the order in which events occur, which helps students follow the storyline or the logical flow of informational texts. For example, when reading a historical account, encourage students to create a timeline of events. This visual representation aids in grasping the progression and significance of historical milestones, making the narrative easier to understand and remember.
Start with these sequencing worksheets:
Begin here
12. Encouraging Predictive Reading
Predictive reading engages students by encouraging them to guess what might happen next in a story based on context clues and their own experiences. This strategy makes reading an interactive experience, stimulating students’ curiosity and engagement with the text. For instance, pause at a suspenseful moment in a story and ask students to predict the outcome. Discussing their predictions fosters a deeper engagement with the text and illustrates how to get better at reading comprehension by actively thinking ahead.
Begin here:
Begin here
13. Understanding Author’s Purpose
Identifying why an author wrote a piece — to inform, persuade, entertain, or explain — is fundamental in analyzing and understanding complex texts. Discussing the author’s purpose helps students see beyond the surface of the text and consider the underlying messages or arguments. For example, when reading an article about conservation, ask students to determine if the author’s purpose is to inform about conservation issues, persuade readers to take action, or both. This recognition enhances comprehension and critical thinking about texts.
Use these worksheets to strengthen comprehension of the author’s purpose:
Begin here
14. Point of View Analysis
Analyzing the narrator’s or characters’ perspectives in a text enriches students’ understanding and empathy. Point of view analysis encourages students to consider how the story might change if told from a different perspective. For instance, reading a story first from one character’s point of view and then another’s can reveal biases, motivations, and unseen aspects of the story. This exploration deepens comprehension and teaches students to consider multiple perspectives.
Start with these POV analysis worksheets:
Begin here
15. Character Analysis
Character analysis involves examining traits, actions, and motivations to understand characters deeply. Through such analysis, students learn to infer character traits from actions and dialogue, adding layers to their comprehension. For example, discussing why a character made a particular choice or how their actions affect the plot encourages students to connect with and reflect on the characters, fostering a richer reading experience.
Begin with these character analysis worksheets:
Begin here
16. Critical Thinking in Evaluating Arguments
Teaching students to critically evaluate arguments and evidence in texts equips them with the ability to discern reliable information and form their own opinions. This skill is especially important in an era of information overload.
Encourage students to identify claims in a text and the evidence supporting those claims. For instance, in an article arguing for less screen time for children, have students assess the strength of the evidence presented. This critical examination is a key component of how to get better at reading comprehension, as it requires students to engage deeply and thoughtfully with the text.
Begin with these argument evaluating worksheets to enhance critical thinking:
Begin here
6 Parental Strategies for Enhancing Reading Comprehension
1. Utilize Online Reading Games
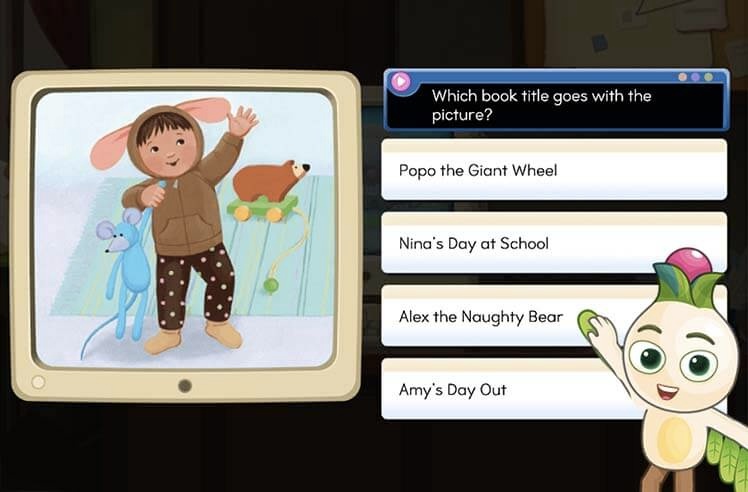
Online reading games are designed to enhance comprehension in a fun, interactive way. These games focus on specific skills such as vocabulary, sequencing, and main idea identification. By incorporating these games into your child’s screen time, you can help them learn how to get better at reading comprehension through engaging activities that don’t feel like traditional homework.
2. Incorporate Practice Worksheets

Another effective strategy on how to work on reading comprehension is through the use of practice worksheets. Available on SplashLearn, these worksheets target specific comprehension skills like summarizing, inferring, and understanding cause and effect. Set aside time for your child to complete these worksheets and then review them together, discussing any challenges they faced and celebrating their successes.
3. Engage in Daily Reading Activities
A fundamental approach to how to practice reading comprehension is by establishing a daily reading routine. Choose a variety of books that interest your child and dedicate a quiet time each day for reading together. After reading, discuss the book, asking questions about the characters, plot, and what they learned. This practices comprehension skills and turns reading into a shared, enjoyable activity.
Related Reading: Best Reading Activities That Turn Kids into Book Lovers
4. Create a Reading-Friendly Environment

Creating a reading-friendly environment at home is essential in how to improve reading comprehension. This involves having a variety of reading materials available, including books, magazines, and newspapers, suited to your child’s age and interests. Also, model the behavior by reading yourself; seeing parents engaged in reading can motivate children to pick up the habit.
5. Discuss Real-Life Connections
Connecting the text and real-life experiences can significantly boost comprehension skills. After your child reads a story or article, ask them how it relates to their own life, events they’ve heard about, or other stories they’ve read. This helps solidify their understanding and encourages them to think critically about the text.
6. Encourage Writing Summaries
Encouraging your child to write short summaries of their reading is a fantastic way to reinforce comprehension. This exercise helps them distill the main ideas and supporting details from texts, improving their ability to identify and articulate key points.
Conclusion
Mastering how to improve reading comprehension is a journey that involves consistent practice, engagement, and the right strategies. By incorporating the techniques discussed in this blog, educators and parents can significantly enhance children’s ability to understand and retain what they read.
Related Reading: Best Reading Comprehension Activities for Kids
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why am I struggling with reading comprehension?
Struggling with reading comprehension can result from various factors, including limited vocabulary, lack of background knowledge, or difficulty focusing and retaining information.
What are the 5 steps that should be taken to improve reading comprehension?
- Increase your vocabulary through regular reading.
- Practice summarizing texts to grasp the main ideas.
- Ask and answer questions about what you’ve read.
- Make connections to personal experiences or other texts.
- Use graphic organizers to visualize information and structure.
How do you fix poor reading comprehension?
Improving poor reading comprehension involves practicing targeted reading strategies, expanding vocabulary, engaging in discussions about texts, and gradually increasing the complexity of reading materials.
What is the root cause of poor reading comprehension?
The root cause of poor reading comprehension often lies in factors such as limited vocabulary, lack of practice, difficulties with decoding words, or cognitive challenges affecting information processing.
What are the three factors that affect reading comprehension?
Three major factors affecting reading comprehension are:
- Reader’s vocabulary and language proficiency.
- Reader’s prior knowledge and experience with the topic.
- Text complexity and structure.






































































