- Introduction: Multiplying & Dividing Fractions
- Introduction: Multiplying Fractions
- First Step to Multiplying Fractions: Modelling
- Multiplying Fractions: 4 Easy Steps
- Analysis: Multiplying Fractions versus Whole Number Multiplication
- Dividing Fractions in Real Life: Introduction
- First Step to Dividing Fractions: Modelling
Introduction: Multiplying & Dividing Fractions
Tough Creatures – the Fractions!
Fractions are considered one of the trickiest math concepts for young kids because they have different notations than whole numbers. It is an abstract notion that challenges the little rockstars to do better.
Math & ELA | PreK To Grade 5
Kids see fun.
You see real learning outcomes.
Watch your kids fall in love with math & reading through our scientifically designed curriculum.
Parents, try for free Teachers, use for free
Operations on fractions add to the complexity as it becomes strenuous for children to understand what these operations mean; therefore, visualizing them can lead to better comprehension of the concept. The multiplication and division of fractions might contradict the existing understanding of multiplying and dividing whole numbers.
For example, multiplying two whole numbers always results in a greater product, but this is not true with multiplying fractions.
Similarly, dividing two whole numbers usually results in a smaller quotient than the dividend, but this is not the case with dividing fractions.
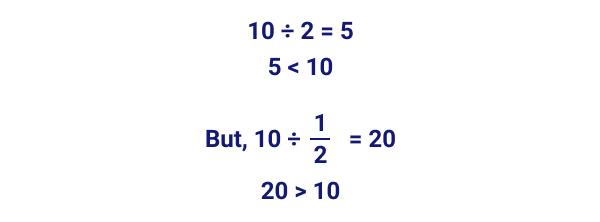
Due to the lack of proper understanding of these concepts, even among teachers, students have difficulty understanding fractions. It also causes confusion and misconceptions among them.
This article aims to provide engaging methods to help children visualize multiplication and division concepts. Furthermore, we will also try to ease the understanding of procedures involved in multiplying and dividing fractions through a simple methodology involving just 4 steps.
Read on and make learning fractions easy and pleasant!
Glossary
- Fraction – Part of a whole number written in the form of a/b
- Denominator – The bottom number on a fraction
- Numerator – The number on the top of a fraction
- Unit Fraction – A fraction with numerator 1
- Whole Number – Counting numbers (0, 1, 2, 3, 4 …)
- Equivalent fraction – A fraction that has equal/same value as another fraction
- Simplifying – Making a fraction simpler
- Proper fraction – A fraction with a value less than 1 (numerator < denominator)
- Improper fraction – A fraction with a value greater than 1 (numerator > denominator)
- Mixed Number – A way of writing improper fractions using a whole number and a proper fraction
- Divisor – A number by which another number is to be divided
- Dividend – A number that is to be divided
- Quotient – The result of dividing one number by another
- Remainder – The leftover after division
Starting with the Multiplication & Division of Fractions: Must-Knows
- Understanding of multiplication and division with whole numbers
- Understanding of fractions and their visual models
- Representing whole numbers as fractions
- Equivalent fractions
- Simplifying fractions to their lowest form
- Conversion of improper fractions into mixed numbers and vice versa
- Addition of fractions
Related Reading: Best Math Apps to Make Math Exciting for Students
Introduction: Multiplying Fractions
Before starting with the steps of multiplying fractions, it is imperative to develop a conceptual understanding of fraction multiplication. Children should be able to visualize multiplication and know what it means to multiply a fraction by a whole number or a fraction.
Quick Tip: Start with modeling multiplication or division involving only whole numbers. You can then move on to fractional numbers. This way, kids’ knowledge of multiplying or dividing whole numbers will be refreshed, and they can connect it to constructing the models for fraction multiplication or division.
Let’s start with fraction multiplication.
First Step to Multiplying Fractions: Modelling
Using visual models as a learning aid makes teaching and learning more effective, fun, and interactive. It is a student-centered approach that helps kids visualize key mathematical concepts, which further aids them in gaining a deeper understanding of the concept at a root level.
For the teachers, visual models can trigger discussions of mathematical ideas and relations with previously known concepts. It helps them better understand the students’ grasp of the concept.
Therefore, teaching fraction multiplication initially through models and then proceeding toward standard procedures would be the ideal approach.
To begin with, Fraction Multiplication can take 3 different forms.
Level 1A: Whole × Fraction
Level 1B: Fraction × Whole
Level 2: Fraction × Fraction
Please note: We will not take up mixed numbers as a separate case because these are also fractions written differently. To help your kids learn about mixed numbers and improper fractions through fun math games online, you can sign up here!
Level 1A: Whole × Fraction
Example 1: Tim used ¼ of the pumpkin to make one pumpkin pie.
He made 3 pies. Let’s find out how many pumpkins he used in total.
As he used one-fourth of the pumpkin 3 times, its multiplication expression would be 3 × ¼
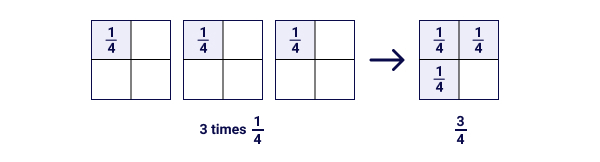
So,
3 × ¼ = 3/4
So, Tim used three-fourths of the pumpkin to make 3 pies.
Example 2: If Tim had to make 5 pies, how many pumpkins would he need?
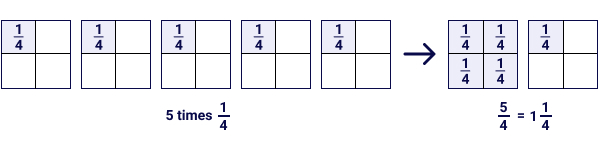
5 ×¼ = 5/4
So, Tim would need 1 whole and a quarter piece of the pumpkin to make 5 pies.
Level 1B: Fraction × Whole
Visualizing the model for Fraction × Whole could be challenging for kids.
First, the first number in the multiplication sentence denotes the number of groups or times something is to be repeated. But, in the Fraction × Whole scenario, how do we form groups in a fractional number?
Example: ¼ × 8
We can describe this expression in simple words as one-fourth of eight. Mathematically, the word ‘of’ means multiplication.
Let’s draw a model for this expression.
Step 1:
Step 2:
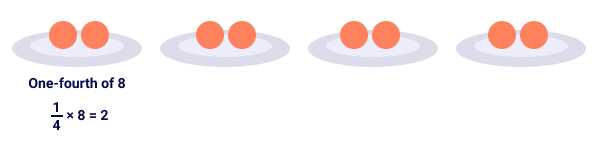
So, ¼ × 8 = 2
Example 1: ¾ × 8
This means three-fourths of eight
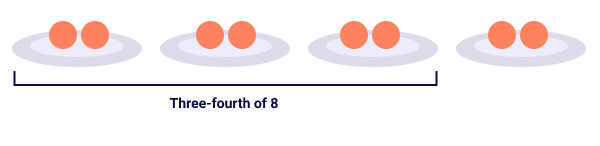
So, ¾ × 8 = 6
Let’s try a few more examples.
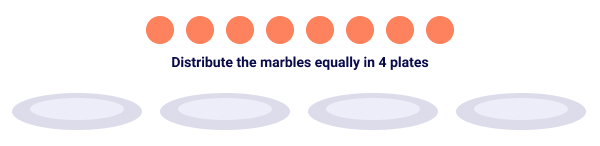
Example 2: Jamie prepared 4 glasses of juice using 3 limes. Find the number of lime fruits he used for each glass of juice.
He used a quarter of 3 limes to prepare one glass of juice.
Mathematical expression to be solved for this example: ¼ × 3
Let’s consider the three limes to be A, B, and C.
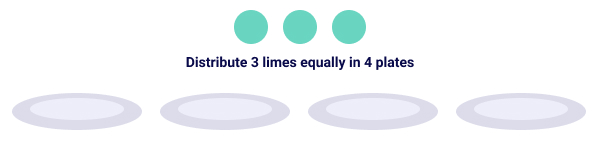
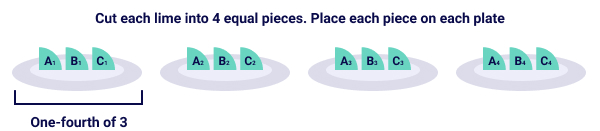
Each plate represents one-fourth or quarter of the whole lot, 3 limes.
How many fourths are there in one plate? Three-fourths
So, ¼ × 3 = ¾
Jamie used ¾ of lime in one glass of juice.
Example 3: Find out how many limes Jamie used for 3 juice glasses.
This means we need to determine how much three-fourths of 3 limes is.
Mathematical expression to be solved for this situation: ¾ × 3
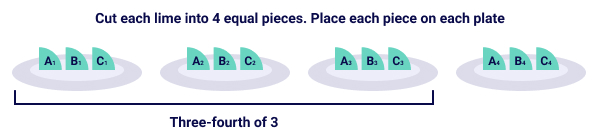
Each plate represents one-fourth or quarter of the whole lot i.e. 3 limes. So, three plates will represent three-fourths.
How many fourths are there in 3 plates? Nine-fourths

So, ¾ × 3 = 9/4
Jamie used 9/4 limes in three glasses of juice.

Level 2: Fraction × Fraction
Multiplying a fraction with a fraction is also a tricky form, and students find it quite difficult to understand the application of multiplying two fractions.
We can help them visualize this concept through this engaging and simple paper-folding activity.
Example 1: Visualize and solve: ⅓ × ½
In general, this expression would mean one-third of the half. You can help your child model this scenario using a sheet of paper.
Ask your little learner to follow these simple steps:
- Take a rectangular sheet of paper and fold it in half.
- Next, fold the half into 3 equal parts.
- Color one of the folded sides to show one-third of the half.
- Open the sheet back up.
- Identify which fraction of the whole the shaded part represents.
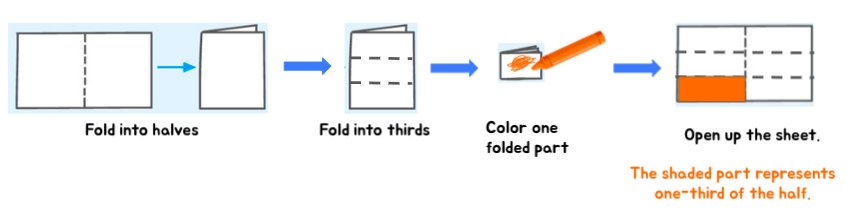
⅓ × ½ = ⅙
MUST TRY MORE!
Encourage your children to try multiplying different fractions using the same technique.
Let’s explore a few more examples:
The following models follow the same principle as in the paper folding activity above. The principle mentioned is modeling two fractions in one model.
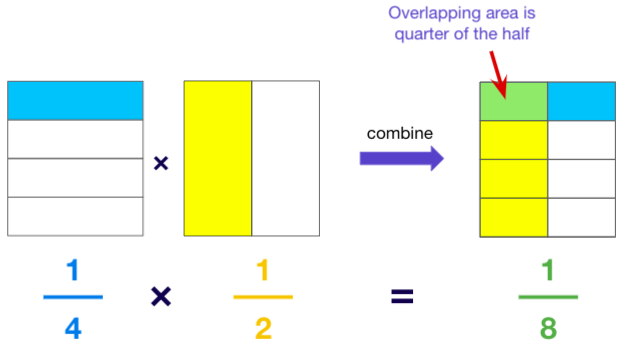
Example 2: How much is ¼ × ½?
This represents a quarter of half.

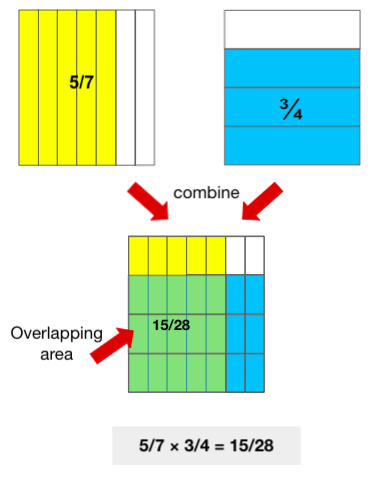
Example 3: 5/7 × ¾
Example 4: 1/3 × 1⅗
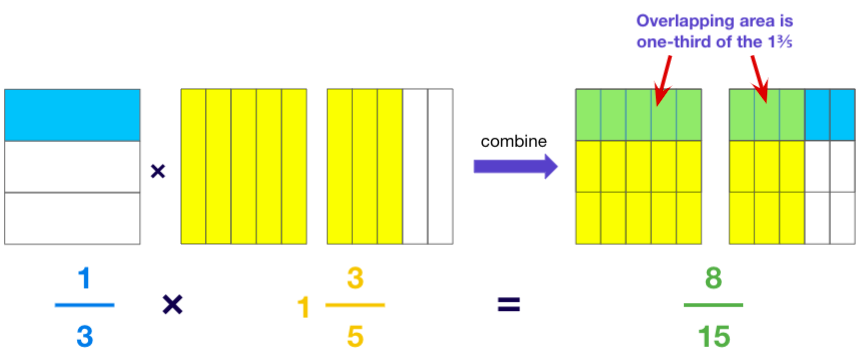
After a few examples, you can encourage your child to draw the combined model directly.
Draw the model to multiply two fractions with these steps:
- Draw a big rectangle.
- Divide it into as many equal horizontal strips as the denominator of the first fraction. Shade parts to represent the first fraction.
- Next, divide the same model into as many equal vertical strips as the denominator of the second fraction. Shade parts to represent the second fraction.
- Identify the overlapping part in the model. The fraction it represents is the product of the two fractions.
Multiplying Fractions: 4 Easy Steps
Encourage kids to observe the products derived from the models and tell them which rule is being followed in multiplying fractions.
We can help them understand the process through these 4 easy steps of multiplying fractions.
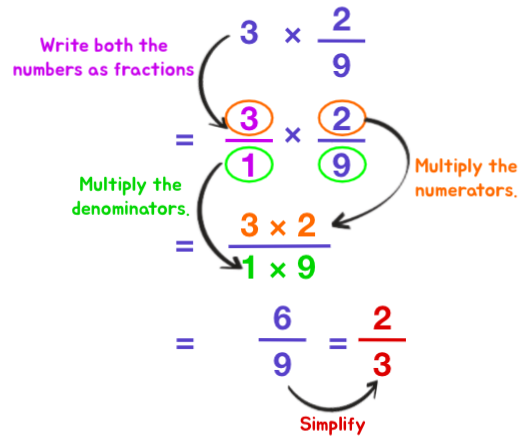
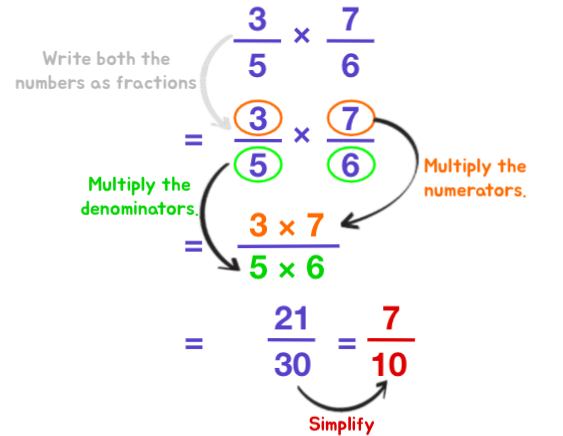
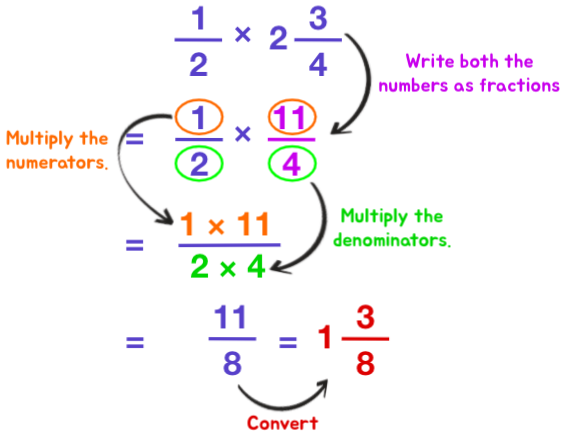
- Write both numbers in fraction form.
- Multiply the numerators. The product is the new numerator.
- Multiply the denominators. The product is the new denominator.
- Rewrite the answer in the lowest or mixed number form.
Check out a few examples.
Example 1:
Example 2:
Example 3:
Analysis: Multiplying Fractions versus Whole Number Multiplication
Question: Do we always get a greater product on multiplying two numbers?
Observe the following multiplication problems.
6 × 4 = 24
2 × 9 = 18
3 × 1 = 3
5 × 7 = 35
10 × 8 = 80
19 × 1 = 19
8 × 0 = 0
7 × 11 = 77
16 × 2 = 32
Do you think the same question holds for multiplication with fractions as well?
The answer to that is ‘sometimes’.
Let’s check out a few cases to understand them better.
Case 1: When one of the multiplicands is 0
The product will also be a zero regardless of the other fraction.
¼ × 0 = 0/4 = 0
⅗ × 0 = 0/5 = 0
7/2 × 0 = 0/2 = 0
Case 2: When one of the multiplicands is a fraction less than 1
The product will be smaller than the other fraction.
3/4 × 7/3 = 21/12 = 7/4 (< 7/3)
1/4 × 7/8 = 7/32 (< 7/8)
3/4 × 1/9 = 1/12 (< 1/9)
Case 3: When one of the multiplicands is a fraction equivalent to 1
The product will be the same as the other number.
1 × 7/8 = 7/8
6/6 × 9/5= 54/30= 9/5
6/6 × 3/5= 18/30= 3/5
Case 4: When one of the multiplicands is a fraction greater than 1
The product will be greater than the other fraction.
8/3 × 2/5= 16/15 (> 2/5)
6/10 × 9/5= 54/50= 27/25 (> 6/10)
9/6 × 1/7= 9/42= 3/14 (> 1/7)
Case 5: When both of the multiplicands are fractions greater than 1
The product will be greater than both fractions.
8/3 × 3/2 = 4 (> 8/3, 3/2)
6/4 × 5/2= 30/8 (> 6/4, 5/2)
Related Reading: Different Types of Graphic Organizers for Teachers and Students
Dividing Fractions in Real Life: Introduction
We come across situations in our day-to-day lives where we apply the concept of fraction division. Fraction division can be made interesting, and the concept can be fully instilled in kids’ minds if they are challenged to solve real-life scenarios.
This would help the kids visualize and make sense of fraction division.
Example: Suppose you have 3 apples, each cut in half. How many people can you distribute these 3 apples if each gets half a piece?
Let’s picture this situation and solve it. After all, an apple a day will certainly keep the math blues away!
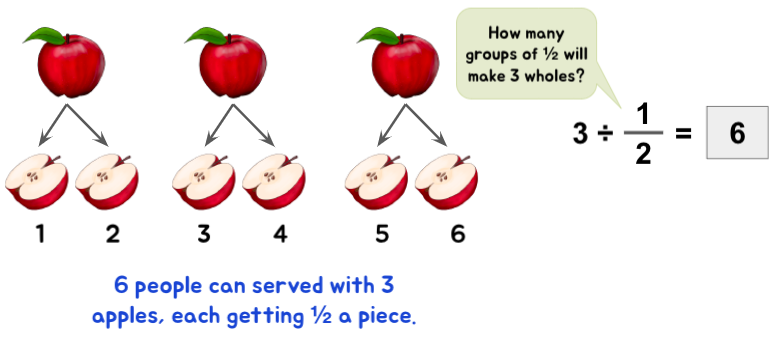
The problem can be further extended by modifying the fraction.
For example, what if you decide to give each person a quarter piece? How many people can be served now?
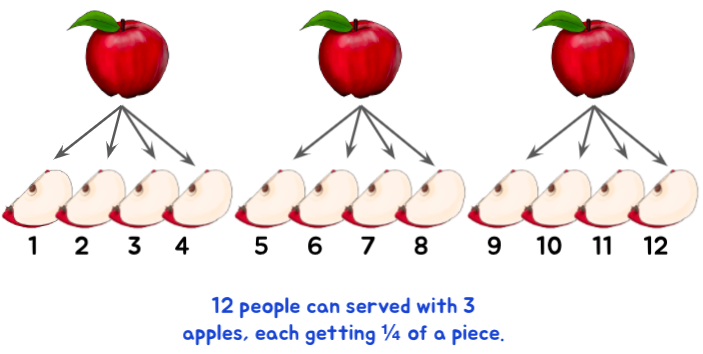
Or what if you decide to give each person three quarters? How many people can be served now?
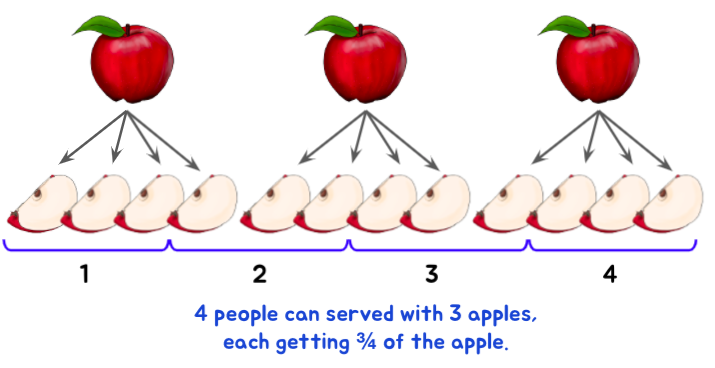
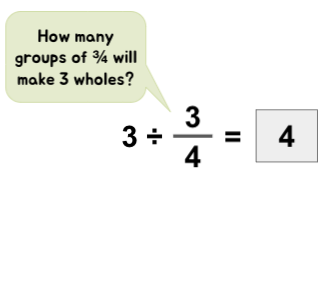
Comprehending and modeling a problem is a crucial step in any problem-solving scenario of fraction division. Encourage students to try visualizing the scenario and then look for its solution.
Draw and Solve!
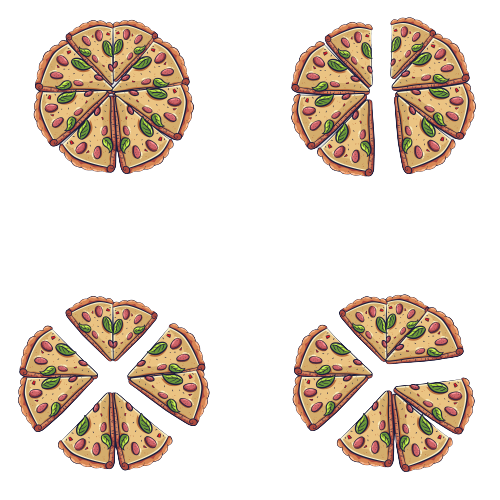

A group of friends bought a pizza. They shared the pizza equally and finished it.
Try identifying how many friends there were if each of them got:
| one-eighth of the pizza | two-eighth of the pizza | |
| 8 friends | 4 friends | |
| So, 1 ÷ ⅛ = 8 | So, 1 ÷ 2/8 = 4 |
First Step to Dividing Fractions: Modelling
Like multiplication, once students gain expertise in modeling division problems for fractions, the method to find the answer is a cakewalk.
Therefore, an approach from the visual to the non-visual method is also suggested for the division of fractions. Such an approach is more plausible for students as it lays a strong conceptual foundation.
Let’s see a few examples.
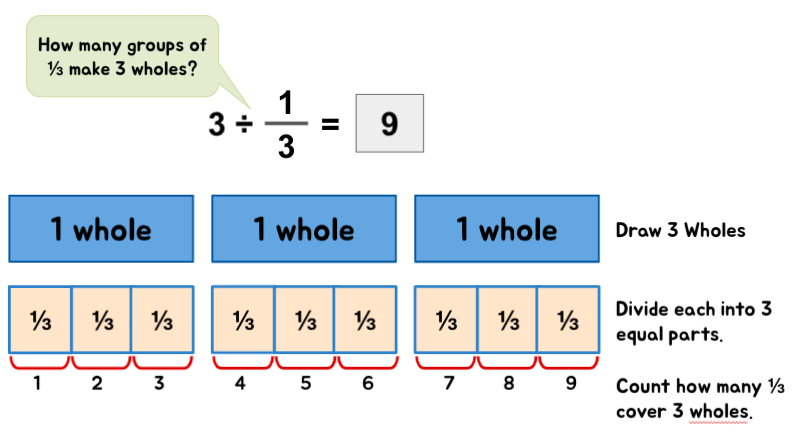
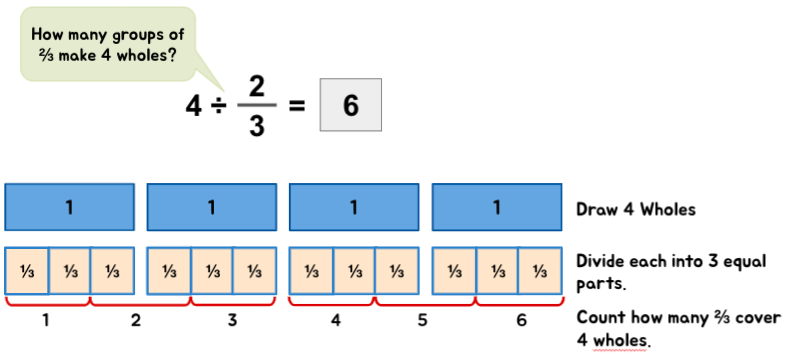
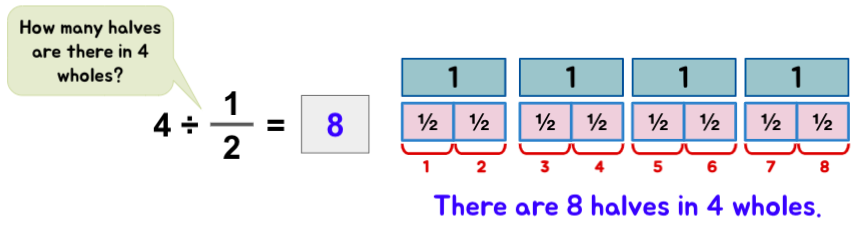
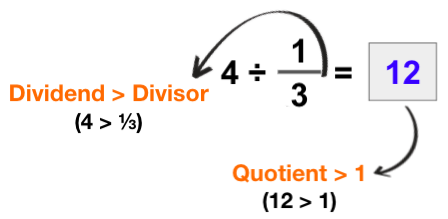
Whole Number ÷ Fraction
Example 1:
Example 2:
Related Reading: The Most Important Math Symbols Students Need to Solve Problems
Quick Tip: When a divisor is a fractional number – it helps to describe the division statements as ‘How many groups of (divisor) can be formed from the (dividend)?’ or ‘How many groups of the (divisor) are there in the (dividend).’ These descriptions help children to visualize the situation at hand with more ease.
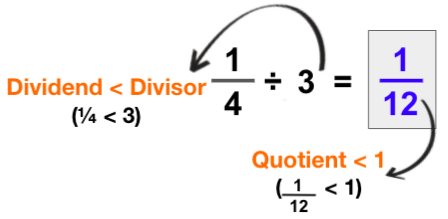
Fraction ÷ Whole
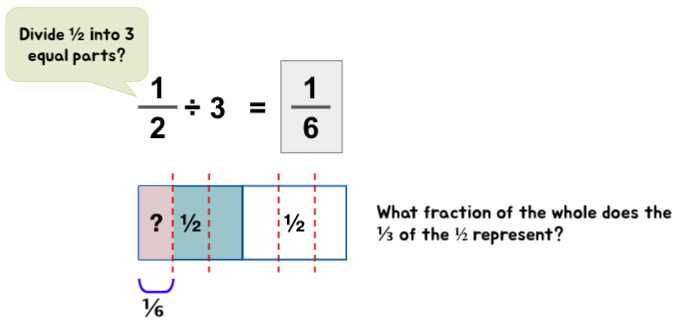
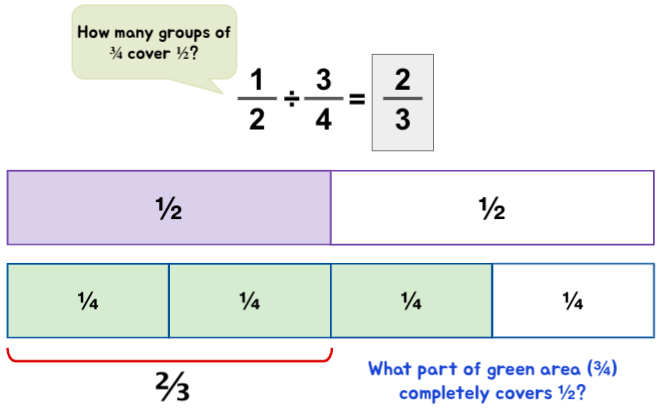
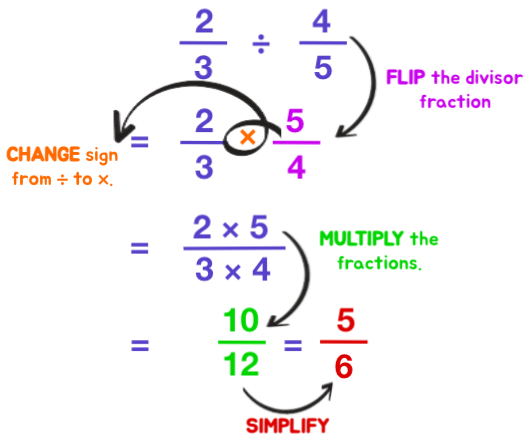
Fraction ÷ Fraction
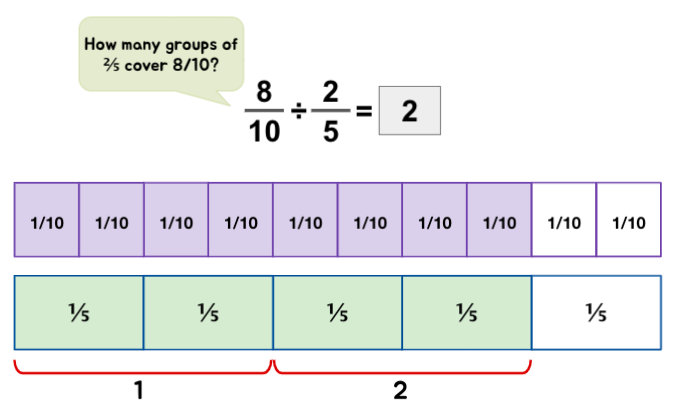
Mixed Number ÷ Fraction
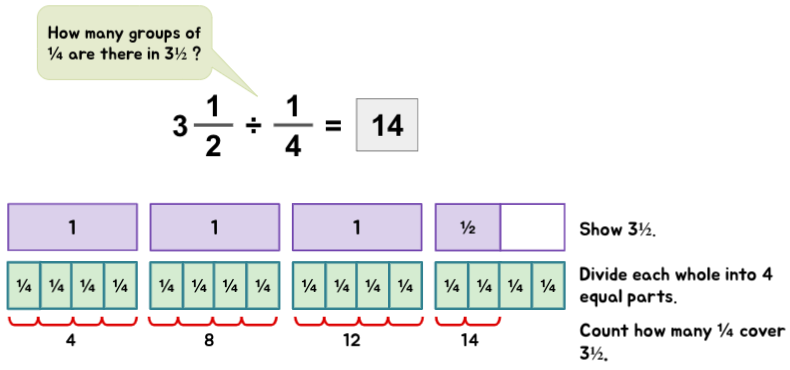
Dividing Fractions that Involve the Remainder
Example 1
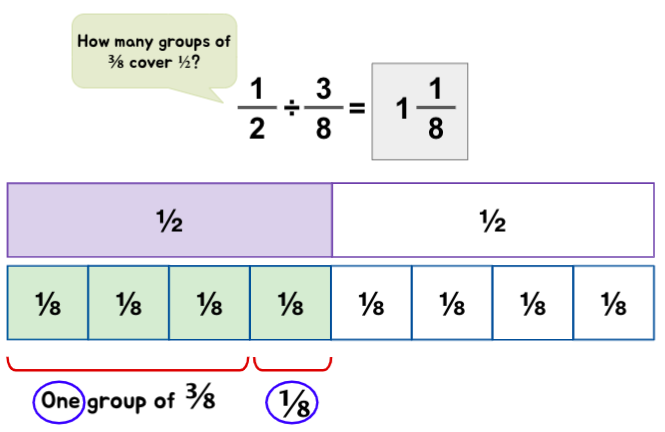
Example 2:
Some Common Struggles in Dividing Fractions
- Students often struggle to understand the difference between dividing by 2 and dividing by ½.
The following models can help them easily visualize the difference.
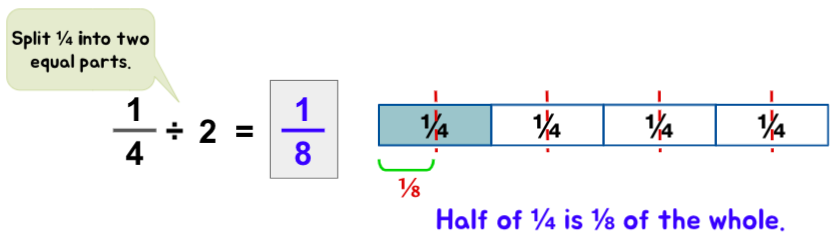
- Students often struggle to understand that the division of fractions will not always result in a smaller quotient.
Dividing Fractions: 4 Easy Steps
We must encourage children to observe the quotients derived from the models and tell them which rule is followed in multiplying fractions. Doing such activities with them can help in developing inference and reasoning skills.
Help them learn the procedure to divide fractions through these 4 easy steps.
- Flip the divisor fraction.
- Change the sign from ÷ to ×
- Multiply the fractions.
- Simplify.
Key to Excel—Practice More
Understanding fractions and their operations becomes much easier once children gain expertise in visualizing the problem and knowing what needs to be calculated. But to gain such confidence, they need to practice a lot of math problems. It’s necessary that they model the problem and then solve it.
You can refer to these worksheets on SplashLearn, which are easily downloadable and printable, to help solidify your kid’s understanding of multiplying fractions.
To sum up
- For a deeper understanding of the concept, provide kids with an environment conducive to experiential learning.
- You can use your kids’ previous and existing knowledge of multiplying and dividing whole numbers to build new knowledge of multiplying and dividing fractions.
- Encourage your kids to visualize problems and model them. Make them feel comfortable with asking questions.
- It’s imperative to focus less on answering accurately and more on the reasoning and thought process of the child.
- As a parent, relate the mathematical problems with real-life situations and provide instances from day-to-day activities.
Make Fractions Easy with SplashLearn
With interactive games and rewards to boost your child’s confidence and scores, you can now make learning easy and seamless. Join our community of 40+ million fearless learners today!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1 – How to multiply fractions step by step?
- Write both numbers in fraction form.
- Multiply the numerators.
- Multiply the denominators.
- Simplify or rewrite the answer in mixed number form.
Q2 – How to divide fractions step by step?
- Flip the divisor fraction.
- Change the sign from ÷ to ×.
- Multiply the fractions.
- Simplify.
Q3 – How do you identify if multiplication by a fraction will result in a greater or a smaller product?
Compare the numerator and denominator of the fraction to check whether the product will be greater or smaller than the number to which they are multiplied.
Greater Product → Numerator > Denominator. Examples: 3/2, 4/3, 8/5, and so on.
Smaller Product → Numerator < Denominator. Examples: 3/4, 4/7, 5/9, and so on.
























