No two days are the same and what might have worked once in a classroom, might not work again. Switching between teaching strategies to suit the needs of the learners is a great way to ensure that the learners are meaningfully engaged and actively participating in the classroom.
Math & ELA | PreK To Grade 5
Kids see fun.
You see real learning outcomes.
Watch your kids fall in love with math & reading through our scientifically designed curriculum.
Parents, try for free Teachers, use for free
Whether you have just begun as a teacher or you have years of classroom experience, you know that creative teaching strategies help students meet their individual needs and hit their full potential.
Every teacher’s classroom practice is unique, so here are effective teaching strategies you can use for inspiration to give your students a fulfilling learning experience.
15 Effective Types of Teaching Strategies for Teachers
1. Gamification

Gamification is among the best teaching strategies that use elements of game design to enhance the learning experience. It is an effective strategy for reinforcing concepts and improving retention.
If you want to introduce gamification into your classroom, SplashLearn is an ideal tool.
- Teachers can use SplashLearn to complement their instructional strategies by providing engaging, game-based practice that aligns with classroom lessons.
- Whether you’re reinforcing a math concept or building reading skills, SplashLearn offers activities that make learning feel like play, all while ensuring students progress at their own pace.
By integrating SplashLearn into your teaching techniques, you can transform your classroom into a vibrant, supportive environment where every student is excited to learn and succeed.
2. Cooperative Learning

Virtual learning has led educators to understand the importance of a key part of the learning process – cooperation.
Cooperative learning is an instructional strategy in which a small group of students collaboratively work on a given task. The task can be as simple as solving a quiz or as complex as writing a story.
In such activities, students of different learning abilities come together and help maximize each other’s potential. It nurtures shouldering the responsibility to contribute to successfully finishing the task. It also encourages students to support one another and pitch in wherever required to achieve the end goal.
Consider this: Split your class into small groups and give them a simple science experiment, like creating a volcano with baking soda and vinegar. Each group member has a role, such as measuring ingredients or recording results.
Related Reading: What is Cooperative Play? Stages, Benefits and Examples
3. Differentiated Instruction
Every classroom is a dynamic learning space with learners of varied abilities and personalities.
Differentiated instruction is a teaching strategy that takes into account that students from a single classroom may be at different starting points in their learning process.
Differentiated instruction needn’t just mean different content to suit individual needs. It can mean a combination of different content, products, teaching aids, methods, or even a different learning environment to help learners succeed.
For example, in an ELA lesson, a teacher might choose to divide the students into two groups based on their decoding and comprehension capacities.
Each group might receive a text that is suited to the group’s ability to grapple with it. While one group may read and discuss their text independently, the teacher might choose to work with the second group to help them read. The two groups may also receive differentiated assessment tools such as worksheets of varying complexity.
This helps address diversity in learning experiences and cater to all the students in an equally engaging way.
Consider this: In a reading lesson, give advanced readers a chapter book while struggling readers work on a simpler text. Both groups can then share what they’ve learned, helping everyone feel included.
4. Visualization
Visualization is very simply put, the ability to create mental images based on the words we hear or the text that we read.
This strategy, if used well, can drastically help students focus on the concept or subject matter at hand. It brings concepts to life and encourages students to make connections to the real world.
Some of the methods of implementing this strategy in the classroom include:
- Use of audio visual aids like photos, videos, audio clips, songs etc
- Diagrams, charts and mind maps
- Modeling as you teach for the visual learners who might need to see a visual representation to understand as opposed to hearing the concept being explained.
Consider this: When teaching the water cycle, show a video of how water evaporates from a lake, forms clouds, and then falls as rain. After watching, ask students to draw their own diagrams of the water cycle.
5. Student Centered Inquiry
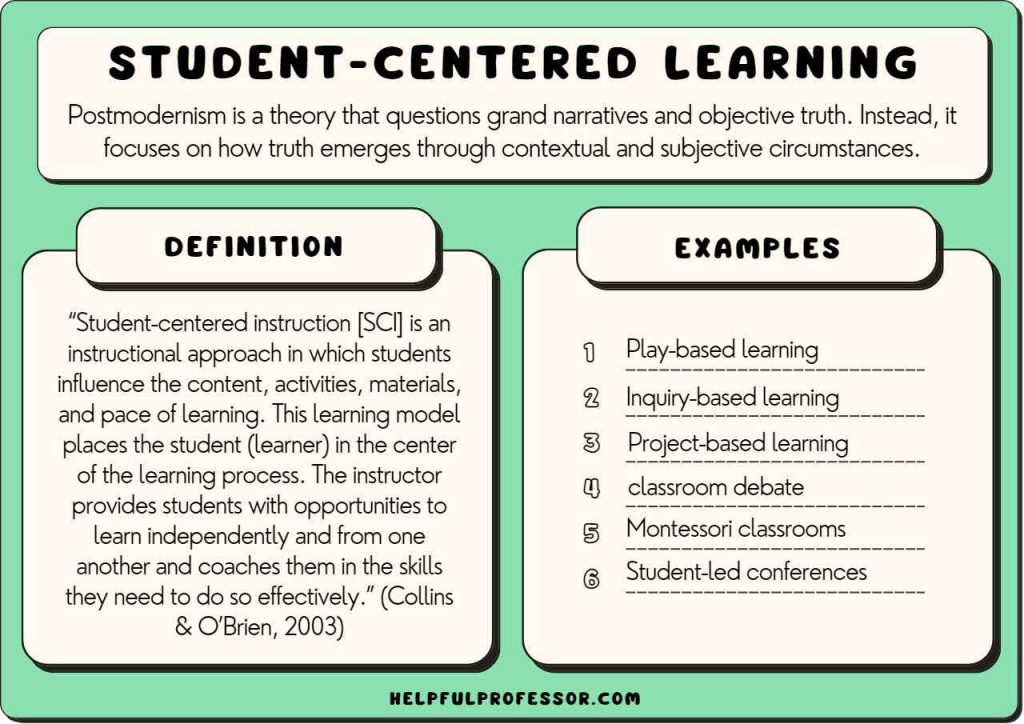
Student-centered inquiry is a method that focuses on the student’s role in the learning process. So, in an inquiry-based classroom, one would see students exploring the material or concept, making sense of it, sharing thoughts and ideas, and asking questions rather than the teacher just orally explaining the concept.
Student-centred learning approaches are a great way to generate curiosity among young learners and engage an inactive class. Through such an approach, children develop skills of researching, co-relating, and reflecting on information through independent exploration and engagement with the content.
Consider this: Let students choose a topic they’re curious about for a mini-research project. They might explore “How do birds fly?” or “Why do leaves change color?” Encourage them to present their findings in any creative way they like.
Related Reading: Best Tips for Creating a Healthy Student-Centered Learning Environment
6. Scaffolding
Scaffolding is an instructional strategy for teachers where complex tasks are broken down into smaller, more manageable parts, with guidance provided at each step. This gradual release of responsibility helps students build confidence and skills, enabling them to complete tasks independently over time. Scaffolding is particularly beneficial if you are looking for teaching strategies for elementary students as it supports their learning at an appropriate pace.
Consider this: When introducing a new math concept, start with guided practice. Walk students through the steps to solve a problem together, then gradually reduce your assistance as they work on similar problems independently.
If you’re looking to explore strategies for scaffolding in the classroom, here’s a detailed article that can help you better understand how to use scaffolding: How to Use Scaffolding Strategies in the Classroom
7. Flipped Classroom
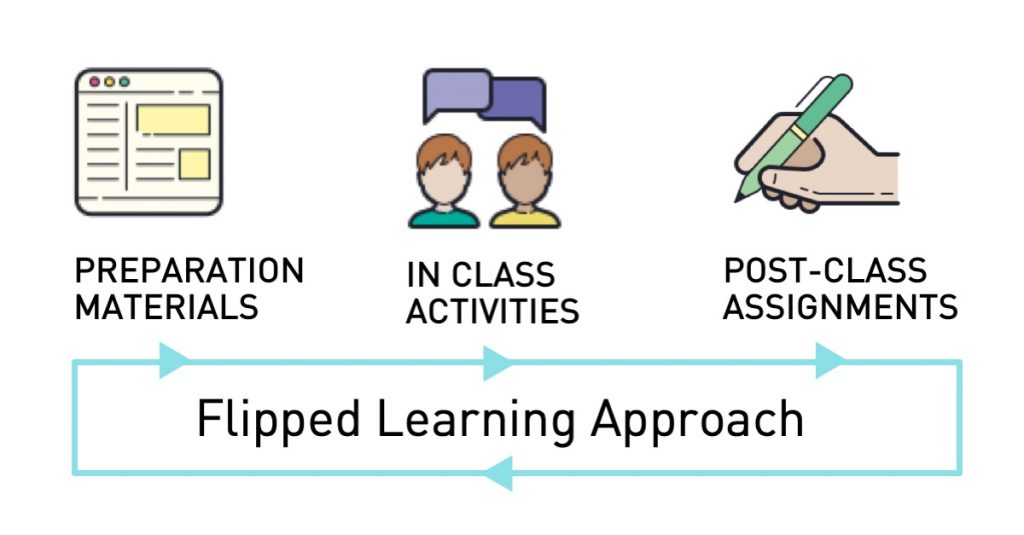
The flipped classroom is one of the core teaching strategies that has gained popularity in recent years. It’s among the best teaching strategies for creating an interactive and student-centered learning experience. In this approach, teachers provide educational materials, such as video lectures or readings, for students to review at home.
Flipped classroom examples include students watching video lessons before class and using their in-class time for discussions, problem-solving, and collaborative projects. This educational strategy encourages self-directed learning and helps students develop critical thinking skills.
Consider this: Assign a short video on fractions for homework. The next day, instead of lecturing, use class time to solve fraction problems together, allowing students to ask questions as they work.
8. Project-Based Learning (PBL)

PBL encourages students to work on extended projects that require them to explore, analyze, and apply their knowledge. This educational strategy promotes critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills.
In a project-based learning approach, students take on complex, open-ended tasks that simulate real-life situations. It’s an effective strategy for teaching by allowing students to delve into topics deeply and develop practical skills that are valuable beyond the classroom.
Consider this: Assign a short video on fractions for homework. The next day, instead of lecturing, use class time to solve fraction problems together, allowing students to ask questions as they work.
9. Mindfulness and Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)

Mindfulness and Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) focus on nurturing students’ emotional well-being and interpersonal skills. Mindfulness practices, like breathing exercises and meditation, are ways of teaching students to manage stress and improve concentration.
SEL strategies involve teaching skills related to self-awareness, empathy, and relationship building. This teaching approach equips students with vital social and emotional skills to handle challenges effectively.
Consider this: Start each day with a 5-minute breathing exercise. Ask students to close their eyes and take deep breaths, focusing on how they feel. This helps them start the day calm and focused.
Related Reading: Interesting Social-Emotional Learning Activities for Classroom
10. Peer Teaching and Peer Assessment

Peer teaching and peer assessment are valuable tutoring strategies that empower students to take an active role in their learning. Peer teaching encourages collaboration and peer-to-peer knowledge sharing, enhancing the overall learning experience.
In this teaching approach, students learn from their peers, reinforcing their understanding of the material. Additionally, peer assessment involves students evaluating each other’s work, which promotes self-assessment and critical thinking.
Consider this: Pair up students and have them explain a math concept to each other, like how to add fractions. Afterward, let them give each other feedback on what they did well and what they could improve.
11. Socratic Questioning

Socratic questioning stimulates critical thinking and meaningful discussion. It’s a way of teaching that encourages students to explore concepts and ideas deeply. By asking thought-provoking questions, educators can guide students to analyze and reflect on the subject matter effectively.
Socratic questioning is a valuable teaching practice that fosters analytical thinking and reasoning skills. It’s a method of teaching that engages students in active dialogue rather than passive learning. This approach helps students grasp complex concepts and encourages them to think critically and express their thoughts.
Consider this: During a discussion on a book, ask open-ended questions like, “Why do you think the character made that choice?” or “What would you have done in their place?” This encourages students to think deeply and share their perspectives.
12. Formative Assessment
Formative assessment is an educational strategy that involves ongoing checks for understanding throughout a lesson or unit. This allows teachers to gauge student progress and make real-time adjustments to their instruction.
By using formative assessments, teachers can ensure that all students are on track and address any misconceptions before they become barriers to learning.
Consider this: Use exit tickets at the end of a lesson where students write down one thing they learned and one question they still have. Review these before the next class to tailor your teaching techniques to meet your students’ needs.
13. Active Learning
Active learning is an effective teaching technique that encourages students to actively participate in the learning process, rather than passively receiving information. This can include discussions, problem-solving activities, and hands-on experiments. Active learning helps students engage deeply with the material, making the learning experience more meaningful and memorable.
Consider this: Instead of lecturing about a science topic, organize a hands-on experiment where students can explore the concept themselves. For example, let them create simple circuits to understand electricity.
14. Think-Pair-Share
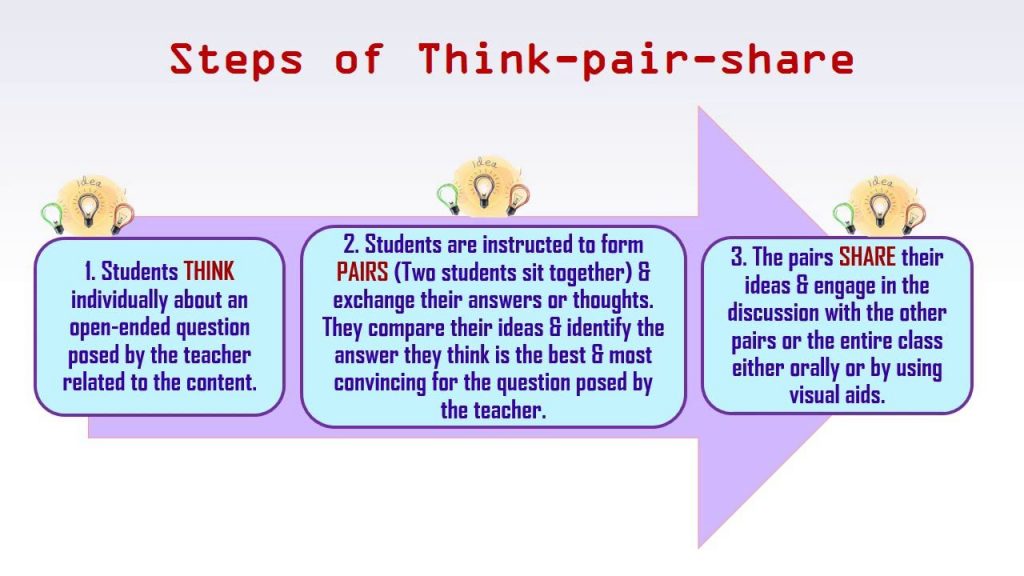
Think-Pair-Share is a teaching strategy that promotes collaborative learning and critical thinking. Students first think individually about a question or problem, then pair up with a partner to discuss their thoughts, and finally share their ideas with the larger group.
Consider this: Pose a question related to the day’s lesson, like “What do you think will happen if we mix these two chemicals?” Give students time to think, then discuss with a partner before sharing their ideas with the class.
15. Differentiated Instruction
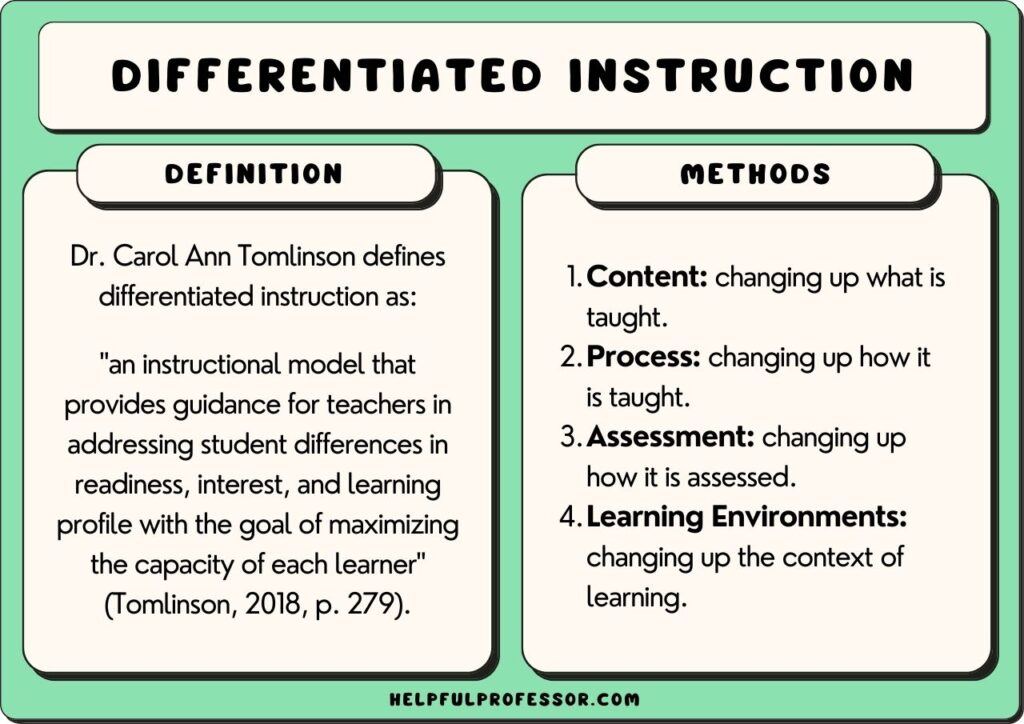
Differentiated instruction is a teaching strategy that recognizes the diverse learning needs of students and adapts teaching methods accordingly. This might involve offering different resources, adjusting the pace of learning, or using various instructional strategies to ensure all students have the opportunity to succeed.
Differentiated instruction is one of the most important educational strategies, especially in classrooms with a wide range of abilities.
Consider this: During a reading lesson, provide a range of books at different reading levels. Allow students to choose a book that matches their ability, ensuring that each student is both challenged and supported.
Related Reading: Best Tips & Strategies to Teach English Language
6 Benefits of Teaching Strategies
Teaching is a dynamic profession that demands a continuous commitment to improving one’s practices in teaching. Here are six key advantages of adopting strategies for teaching:
- Enhanced Learning Through Visualization: One of the most impactful teaching practices is the use of visualization. Employing visual aids such as photographs, videos, and diagrams can help students better comprehend complex concepts.
- Promotes Cooperation: Good teaching techniques often emphasize cooperative learning. Encouraging students to collaborate on projects and tasks not only enhances their academic achievements but also instills valuable teamwork skills.
- Catering to Diverse Learners: Recognizing that students possess varying learning abilities and preferences, effective educators embrace differentiated instruction. This approach allows teachers to tailor their teaching methods to cater to the unique needs of each student, ensuring that all learners have the opportunity to thrive.
- Fosters Student-Centered Learning: Empowering students to take control of their education is a hallmark of good teaching practices. Student-centered inquiry encourages independent exploration, critical thinking, and curiosity.
- Professional Development: Staying current with evolving educational research and teaching methods is crucial for educators. Engaging in continuous professional development through courses and workshops enables teachers to expand their knowledge and refine their teaching skills.
- Promotes Social and Emotional Growth: Effective teaching strategies extend beyond academics to nurture students’ social and emotional well-being. Integrating mindfulness, social-emotional learning, and peer teaching techniques into the classroom environment helps students develop interpersonal skills, emotional intelligence, and a sense of responsibility.
Incorporating these teaching practices into your classroom can create a more engaging and supportive learning environment, ultimately benefiting both teachers and students in their educational journey. By embracing these teaching techniques, educators can foster a positive and enriching educational experience for all.
Conclusion
Every teacher is unique and so is their classroom. So, what might work for your classroom may be entirely different than what may work for your colleagues. By using a combination of educational teaching strategies and changing the mix every once in a while, your classroom is sure to become an enriching environment for you and your students.
What teaching strategies are your preferred choice to include in your practice? Do you have any tips for other teachers? We would love to hear from you, so write to us at help@splashlearn.com
Teaching Younger Learners? Explore These Resources
For tailored strategies on teaching younger students, check out these helpful guides:
- Teaching Preschoolers: Helpful Tips: Practical tips to manage and engage preschoolers.
- How to Teach Kindergarten: Essential advice for creating a nurturing kindergarten classroom.
Related Reading: Best Classroom Management Strategies
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is it important to switch between teaching strategies in the classroom?
Switching between teaching strategies is essential to engage learners effectively and adapt to their evolving needs, ensuring active participation and meaningful learning experiences.
How can technology be used to enhance teaching strategies?
Technology can boost student engagement by introducing online interactive games and educational apps, making learning more enjoyable and effective.
What is differentiated instruction, and how does it benefit students?
Differentiated instruction tailors teaching methods, content, and learning environments to meet the unique needs of each student, ensuring an equally engaging learning experience for all.
What are the 5 E's of teaching strategies?
The 5 E’s of teaching strategies are Engage, Explore, Explain, Elaborate, and Evaluate. These phases guide students through a learning process that encourages active participation and deep understanding of the material.




























