Educational math is an essential subject that is crucial in shaping a child’s future. As students progress through school, math concepts become increasingly complex, requiring them to have a strong foundation of the basics.
Math & ELA | PreK To Grade 5
Kids see fun.
You see real learning outcomes.
Watch your kids fall in love with math & reading through our scientifically designed curriculum.
Parents, try for free Teachers, use for free
Mathematics is not only a subject, it’s a way of thinking.” – Eddie Woo
Math for 4th graders is a critical stage in a child’s math education, as it sets the stage for more advanced math concepts in the years to come. This article will explore the most important 4th grade math topics and provide math tricks for parents to help their children succeed in math.
Although the USA places a high value on studying mathematics as a subject, statistics show that math is also a subject where many students struggle. According to the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP), In 2022, twenty-five percent of fourth-graders performed below the NAEP Basic level. This highlights the need for effective teaching strategies and resources to improve math education in the country.
These statistics highlight the need for students to have a strong foundation in math from an early age. Parents can help their children in flourishing in mathematics and positioning themselves for future success by gaining a knowledge of the fundamental mathematical ideas covered in the fourth Grade. They can help provide support and encouragement, and grasp the topics themselves.
Why Is Math Important?
Math is not just numbers and formulas; it’s a vital tool that surrounds us every day. For example, we use math when we count money, bake cookies or plan our day.
In the fourth grade math curriculum, your child will learn some important concepts like multiplication, division, factors, fractions, decimals and geometry. These skills will not only help them in their academic future but also in their daily lives. Math is not about memorization; it is about critical thinking and problem-solving. By practicing math, kids will develop valuable skills that will help them in all areas of their lives.
Moreover, math deepens our comprehension of the natural and social worlds we live in, and it teaches us how to solve problems, think critically and make decisions. It is a critical skill used in various professions such as building skyscrapers or designing cars. Therefore, it is crucial to motivate and encourage children to learn math stuff for 4th graders by making it fun and exciting.
So, whether your child is a math whiz or still figuring things out, keep encouraging and supporting them. Math is an essential and exciting skill that will help them succeed in life. Remember, in fourth grade, they will learn some critical math concepts that will benefit their future, so keep making math fun and enjoyable!
Related Reading: Most Important Math Concepts Kids Learn in 3rd Grade
7 Math Concepts Every 4th Grader Should Know
Fourth grade math skills are a crucial foundation for advanced math concepts. The Common Core State Standards for Mathematics emphasizes three critical areas for instruction: Developing fluency with multi-digit multiplication and division, understanding fraction equivalence and operations, and recognizing geometric figures and their properties. By mastering these concepts, fourth-graders will be well-prepared for future mathematical studies. Now let’s explore some of the crucial concepts in detail.
1. Multiply Large Numbers
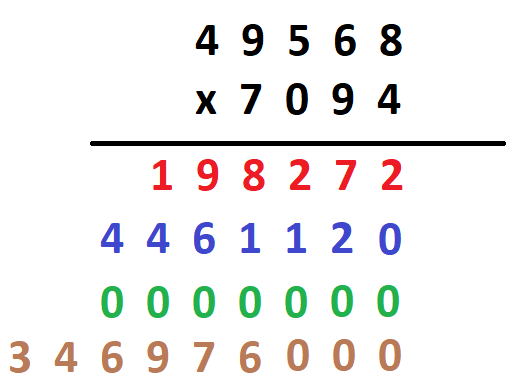
In math for 4th graders, your child will learn how to multiply large numbers, which refers to multiplying numbers that have more than two digits. They will become an expert at multiplying these numbers by learning several approaches, such as the method of partial products, and then practicing those methods until you have mastered them.
2. Divide with Remainders
Your child will learn how to divide larger numbers, which refers to dividing integers with more than two digits. They will be taught how to perform long division. This might be challenging at first, but with enough practice, they will be able to master it. They will also learn how to deal with remainders and understand that remainders represent a fraction of a whole number.
3. Find out the Factors of the Numbers 1–100
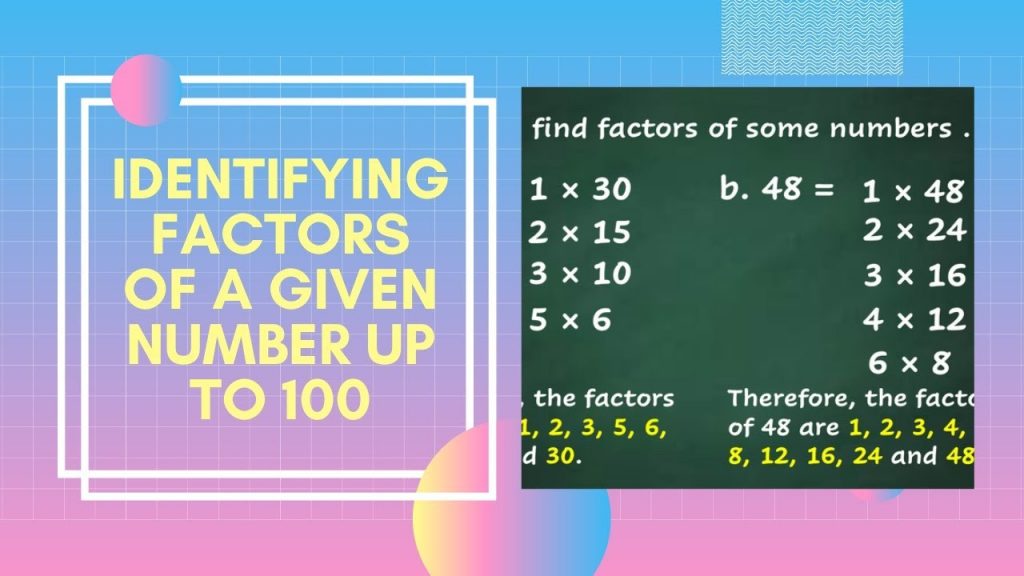
Numbers that, when multiplied together, can produce a desired result are referred to as factors. Your child will learn how to determine the characteristics of numbers up to 100 while they are in the fourth Grade. They will also learn to recognize prime numbers, which are only divisible by one and by the number itself, and no other factors.
4. Solve Real-World Word Problems
Math isn’t just about counting things. Rather, it is about using arithmetic to find solutions to problems that arise in the actual world. In the fourth Grade, students will be taught how to analyze word problems to determine the mathematical procedures that must be applied to resolve them. They will also discover how to validate your responses by analyzing whether or not those responses make logical sense. This is an important skill to have.
5. Understand Large Numbers

As parents and teachers, it’s important to recognize the significance of math for 4th graders. This is the time when they begin to comprehend very large numbers better and develop a strong understanding of place value, which involves recognizing that each digit in a number corresponds to a specific place value. Along with this, they will also learn how to read and write numbers up to billions, which is an essential skill for their academic and practical life.
6. Work with Fractions
In math for 4th graders, students begin to learn how to work on fractions, which is a crucial part of the mathematics curriculum. They will be taught how to add and subtract fractions, locate equivalent fractions and compare them. This is an important skill that will lay the foundation for more advanced math concepts in the future. Moreover, students will also learn how to convert fractions to decimals, a valuable talent that will serve them well throughout their lives.
7. Compare Decimals

It’s important to understand that one of the crucial elements of the math curriculum in Fourth Grade is teaching students how to compare decimal numbers. This skill is essential for their future academic success and in everyday life. By using symbols such as greater than, less than, and equal, students can compare decimal numbers accurately. Additionally, learning to convert between decimals and fractions is another crucial skill that students will gain.
Related Reading: Most Important Math Concepts Kids Learn in 5th Grade
5 Important Math Goals for Fourth Grade
The aim of fourth-grade math instruction is to provide students with a strong foundation in mathematical concepts that they will need throughout their academic and professional lives. The National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) reports that the average math score for fourth grade students in the US rose from 240 in 2017 to 241 in 2019, showing that students are making progress in their mathematical skills. This data suggests that efforts to improve math education in the US are having a positive impact. However, there is still much work to be done to ensure that every student has access to high-quality math education. The following are the key objectives of the fourth grade math curriculum:
- Developing a deep understanding of mathematical concepts helps children to excel in higher-level math courses.
- By using mathematical concepts in real-world situations, children can improve their problem-solving skills, which are useful in all aspects of life.
- Proficiency in the four fundamental arithmetic operations, namely addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, is essential in daily life activities such as shopping, cooking and managing finances.
- Having a solid foundation in fractions, decimals and percentages is crucial for understanding measurements, proportions, and percentages.
- Understanding fundamental ideas about geometry and measurement can help children/students with spatial reasoning and visualization skills, which are important in many areas of life, including architecture, engineering and design.
Overall, math plays a vital role in our lives, and it is your responsibility to ensure that our children have a strong foundation in this subject. Now, let’s figure out what we can do to help them.
Related Reading: Steps for Setting Goals for Kids
How to Help Your Fourth-Grade Child With Math

Math for 4th graders can be challenging at first. However, with proper guidance and consistent practice, students can successfully navigate the fourth-grade math curriculum and develop essential arithmetic skills. These skills will prove valuable in their future academic and personal endeavors.
“Mathematics is a beautiful subject, if taught in a beautiful way.” -Shakuntala Devi
Math for 4th graders is a broad subject that covers several essential topics such as multiplication, division, fractions, geometry and measurement. It is vital for students to commit to memory important mathematical information like multiplication tables and division rules to solve complex arithmetic problems effectively. Though this may seem overwhelming at first, consistent practice helps recall these details quickly.
Fourth-grade math is an excellent opportunity for students to develop critical skills like problem-solving, critical thinking and perseverance. These abilities are all related to mathematics, and real-world situations will challenge students to apply mathematical ideas to find solutions creatively. By practicing regularly and staying organized, students can improve their arithmetic skills and reinforce what 4th graders learn in math class and through homework. Online math tools and games are also great resources to excel in math.
Parents and teachers must encourage and support their fourth-grade students in developing these crucial arithmetic abilities. Doing well in math will have positive effects on their academic success and beyond.
Discover Math Everywhere: How Math is Present in Our Daily Lives
Students learn important fourth grade math facts and skills that help them understand the world around them. For fourth graders, this is the perfect time to discover the magic of math and how it can help them in their everyday lives.
“Mathematics is a way to model the world around us, and to make predictions about what we might observe.” – John Urschel
In fourth Grade, students learn important math facts and skills that help them understand the world around them. They learn about fractions, decimals and geometry, and how they can use these concepts to solve real-world problems. For example, they can use fractions to measure ingredients while cooking or geometry to plan and build their treehouse.
Moreover, fourth graders learn how to calculate and manage money, a critical life skill. They learn how to count money, make changes and organize a budget. These skills will be useful as students start managing their finances.
Fourth graders need to realize that math is not just a subject we learn in school; it is a tool we use every day. By understanding the relevance of math in our daily lives, they can develop a deeper appreciation for the subject and become confident math learners.
So, let’s encourage our fourth graders to discover math everywhere and show them how math can be both fun and useful. With the right mindset and support, they can become math superstars and use their skills to succeed.
Related Reading: Best Classroom Math Games
Exciting World of Fourth Grade Math
Mastering the most important math concepts in 4th grade not only sets a strong foundation for your child’s future academic success but also improves their problem-solving skills and critical thinking abilities. By ensuring they have a solid grasp of concepts like fractions, multiplication, division and geometry, they become ready to approach more complex math problems with confidence. Investing in your child’s 4th grade math education can have a significant impact on their future academic achievements and career opportunities. So, prioritize their education and watch them soar to new heights.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are some of the important math concepts that 4th graders learn?
4th graders learn multiplication and division, fractions, geometry, measurement and data analysis.
How can I help my 4th grader with multiplication and division?
Practice, repetition and real-life examples can help your 4th grader learn multiplication and division. You can also use educational games and online resources.
What are some strategies for helping my 4th grader with fractions?
Visual aids such as fraction bars and circles can be used to teach fractions. Encourage your child to practice identifying and comparing fractions in real-life situations.
What concepts should my 4th grader understand about geometry?
4th graders should be able to identify and classify two-dimensional shapes, understand symmetry and use basic measurement concepts such as perimeter and area.
How can I encourage my 4th grader to enjoy math?
Make math fun by using games, puzzles and real-life examples. Show enthusiasm and interest in math, and help your child understand how math can be useful in everyday life.
























