Educational Mathematics is an essential subject that is integrated into our everyday life. It is a subject that helps individuals develop critical thinking skills and problem-solving abilities that they will use throughout their lives.
Math & ELA | PreK To Grade 5
Kids see fun.
You see real learning outcomes.
Watch your kids fall in love with math & reading through our scientifically designed curriculum.
Parents, try for free Teachers, use for free
“Pure mathematics is, in its way, the poetry of logical ideas.” – Albert Einstein
In math for 3rd graders, several critical math concepts are introduced that serve as the foundation for future learning. This guide will discuss why math is important for third-graders, important third-grade math concepts, third-grade math objectives, and ways to help your child with third-grade math.
Third graders are introduced to several critical math concepts that they need to master before moving on to fourth grade. The mastery of important third grade math facts is critical because they will serve as the building blocks for future math courses. Let’s explore how each third grade math concept helps build your child’s base of quantitative abilities and how you can help make math easy for your children to learn and understand.
Explore Math Games for Third Graders!
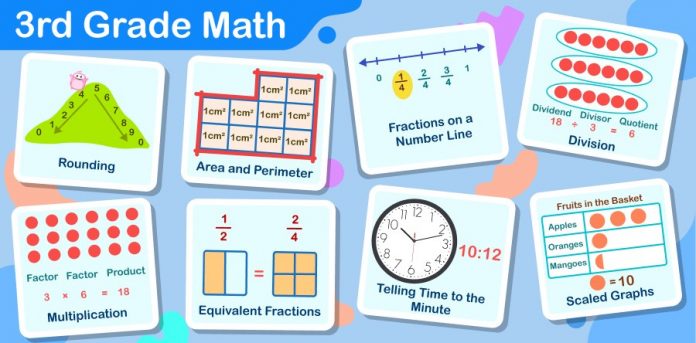
9 Important Third Grade Math Concepts
Important Third Grade Math Concepts are the building blocks for a solid foundation in math education. These concepts include basic arithmetic operations, fractions, and measurement. Mastery of these concepts sets the stage for success in later math courses.
“The only way to learn mathematics is to do mathematics.” – Paul Halmos
The following is a list of the important third-grade math concepts:
1. Multiplication and Division
Multiplication and division are essential math stuff for 3rd graders to master. Students must learn multiplication and division facts and develop the ability to solve problems using these operations. Multiplication and division are used in several real-life settings, making it imperative that students master these concepts.
Before tackling more abstract division and multiplication problems, they first examine each operation using visuals and tangible items. Third graders will continue working on their multiplication and division facts, using language like “product” (the response to a multiplication or division problem), “quotient” (the solution to a division problem), remainders, etc.
They will also relate multiplication to division. Students in the third grade must comprehend how multiplication and division work together. Third graders discover how multiplication and division are related in the same manner that subtracting and adding are inverse operations.
2. Fractions on a Number Line
Fractions on a number line are another critical concept in math for 3rd graders. Students must learn to identify fractions on a number line and understand the relationship between fractions. This concept serves as the foundation for future learning in fractions.
For plotting fractions on a number line, one must find the denominator in the fraction, which is the total number of parts. To locate a fraction on a number line, your kids will learn how to count the number of spaces between each whole number and divide it by the denominator. Students need to understand that fractions represent part of a whole.
3. Measurement and Data
Measurement and data are essential math concepts for third graders to master. Students must learn to measure length, weight, and capacity and understand the relationship between different units of measurement. They must also learn to collect, organize, and interpret data.
In the third grade, math lessons teach students how to measure and estimate time intervals, liquid quantities, and item masses. Third graders will continue measuring with standard units such as inches, feet, yards, centimeters, decimeters, meters, and kilometers. They will also learn to measure temperature in Fahrenheit and Celsius using a thermometer.
In addition to measurement, students will learn about data representation. They will draw scaled picture graphs and scaled bar graphs to represent a data set with several categories.
4. Geometry
Geometry is another critical math concept for third graders. Students must learn to identify and classify shapes, understand the relationship between shapes, and understand basic geometric concepts such as lines, angles, and symmetry.
In third grade, students learn about geometry and focus on two-dimensional shapes. They learn to categorize, analyze, and compare shapes such as parallelograms, rhombuses, rectangles, squares, and trapezoids. Students also learn to define shapes using attributes such as the number of sides and angles.
Parents can help their children find examples of different shapes in their environment to reinforce learning at home, such as rectangles in windows or circles in wheels. You can also encourage their children to draw different shapes and identify their attributes.
5. Word Problems
Word problems are a critical concept in math for 3rd graders. Students must learn to solve problems using critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Word problems help students apply math concepts to real-life situations and develop the ability to think critically and solve problems.
They help students understand mathematical concepts by relating them to everyday life. Third-grade word problem worksheets include addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and fraction word problems. These worksheets should be attempted after a student has studied the underlying skill.
Word problem games can cover a variety of 3rd grade math topics such as area and perimeter, measurement, elapsed time, money, and fractions. Multi-step word problems incorporate addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, time, money, and fractions.
Incorporating third-grade math word problems into daily lessons is a great way to initiate the stage for learning. Starting your daily math lesson with a Math Word Problem of the Day builds confidence in critical thinking skills and creates a learning community. Kids will become accustomed to reading slowly for significance and highlighting important details. To assist them when they are stuck, teach your students to write out equations and illustrate what they mean.
6. Time to the Minute
Time to the minute is another essential concept in math for 3rd graders. Students must learn to tell time to the nearest minute and understand the relationship between seconds, minutes, and hours. This concept is used in several real-life settings, making it imperative that students master it.
By this grade, students should be familiar with telling time and should be able to read both digital and analog clocks. To tell time to the minute, students need to understand that there are 60 minutes in an hour and that a tick mark on the clock face represents each minute.
Teachers use various resources such as videos, games, and hands-on activities to teach this concept. Students should be directed to focus on identifying start times, end times, and elapsed time. Students practice these skills on digital clocks, analog clocks, and time on a line. Many games and hands-on activities are available to keep students engaged in this topic.
7. Scaled Bar and Picture Graphs
Scaled bars and picture graphs are essential math concepts for third graders to master. You should teach students to read and interpret scaled bar and picture graphs and use them to solve problems.
Students learn to read, interpret, and generate categorical data presented in graphs. They also learn how to draw a scaled picture and bar graphs to represent a data set containing more than one category.
Scaled graphs are used to display information with large numbers. Students use the data displayed in scaled bar graphs to solve “how many more or less” issues. They also use the information presented on the axes of the bar graph to read the graph.
They first engage with single-unit scale pictures and bar graphs to prepare students for work with scaled bar graphs. This helps them understand how picture graphs and bar graphs are alike and how they are different. Students learn that a picture graph uses pictures or symbols to represent data, while a bar graph uses bars of equal width to show amounts or frequency.
Understanding scaled bar and picture graphs is essential for students’ ability to collect, organize, analyze, and interpret data. These third grade math skills will be useful throughout their academic careers and daily lives.
8. Area and Perimeter
Area and perimeter are critical math concepts for third graders. Students must learn to calculate the area and perimeter of two-dimensional shapes and understand the relationship between the two.
Perimeter is the distance around a shape, while the area is the amount of surface that a shape covers. Architects, engineers, graphic designers, and people in general use knowledge of area and perimeter on a daily basis.
You add together the lengths of all the sides of a polygon to find its perimeter. Depending on the shape, multiple formulas are used to calculate a polygon’s area. For example, for the area of a square or rectangle, you multiply its length by its width. To find a triangle’s area, multiply its base by its height and then divide by 2.
Area and perimeter are used in everyday life. For example, when buying new land or carpeting for a room, knowing how much space needs to be covered is important. In conclusion, understanding these concepts will help students develop spatial reasoning skills that will be useful throughout their lives.
9. Rounding Off
Rounding off is another essential concept of math for 3rd graders. Students must learn to round numbers to the nearest ten, hundred, and thousand and understand the relationship between rounding and estimation.
Rounding off involves approximating a number to the nearest ten or hundred. The thumb rule for rounding off is that if the number you are looking to round is followed by a 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9, then you should round up. If you are rounding off a number that is followed by a 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4, then you should round down.
Before teaching rounding off to third-grade students, it is important to ensure that they have a solid understanding of place value. Teachers usually begin with two-digit numbers and gradually increase their students’ understanding of rounding by using specific daily objectives that increase in difficulty.
One way to introduce rounding off is using a blank number line showing ten numbers (i.e., numbers 30 through 40). The teacher plots the given number (i.e., 34) on the number line and discusses the tens the number falls between.
At home, you can also use visual models such as modified hundreds of charts to reinforce place value and help conceptualize rounding numbers. Number lines are powerful tools for teaching rounding off because they help students build connections between concrete materials and more abstract models.
Students should have a solid understanding of place value before introducing this concept. They can use visual models such as modified hundreds of charts and blank number lines as well as precise language when asking questions about which ten or hundred a number is nearest to.
Related Reading: Most Important Math Concepts Kids Learn in 4th Grade
4 Reasons Why Math Is Important?
Learning math is crucial for children and mastering 3rd-grade math concepts is an important step in their mathematical development.
“Mathematics is not about numbers, equations, computations, or algorithms: it is about understanding.” – William Paul Thurston
Math is important for problem-solving and decision-making in everyday life. It’s also essential for future career prospects, with job opportunities requiring mathematical skills projected to increase by 31% in the next decade according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. Building a strong foundation in math at an early age by understanding important math concepts can help students prepare for their future.
Here are a few key points related to 3rd-grade math importance.
- Math helps kids develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills, which are important for success in many areas of life.
- Third-grade math concepts lay the foundation for more advanced math topics that kids will learn in the future, such as algebra and geometry.
- Math is used in many real-life situations, from cooking and shopping to building and construction, so understanding math concepts is important for practical everyday tasks.
- Learning math in 3rd grade helps kids develop a positive attitude towards math, which can help them continue to enjoy and excel in math.
Mastering the important math concepts taught in 3rd grade prepares children for more advanced math and helps them develop valuable skills that will benefit them throughout their lives. With this in mind, let’s take a closer look at the specific objectives and learning goals for 3rd grade math.
Related Reading: Best Math Games for Kids That Are Fun to Play
Third Grade Math Objectives

After covering ‘What do 3rd graders learn in math?’, it is important to understand the objective of this set curriculum. The primary objective of third-grade math is to help students develop a solid foundation in mathematical concepts and operations. Third graders must be able to understand and apply the mathematical concepts they learn in real-life settings. They must be able to solve problems using critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Additionally, third graders should be able to communicate mathematical ideas and reasoning effectively.
Proficiency in math is a major concern for third-grade students as it forms the basis of their future mathematical learning. To establish a strong mathematical foundation, it’s important for third-graders to grasp key concepts like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. The 3rd-grade math curriculum is designed to focus on developing this foundation, with an emphasis on basic arithmetic operations.
According to an article by Northern Illinois University’s Department of Mathematics, math is not just a subject to learn in the classroom, but it’s an essential tool for everyday life. The article emphasizes the real-world applications of math and encourages teachers to help students understand its importance outside of the classroom. Teachers can make use of interactive and engaging activities to build math skills and make math fun.
The third-grade math curriculum covers the base-ten numeration system, mathematical operations, fractions, and fundamental arithmetical operations. Additionally, it focuses on developing students’ critical thinking and reasoning abilities. The curriculum also introduces the fundamentals of algebra, including rules for solving algebraic equations, the direction and sequence of operations, and the use of symbols to determine the relationship between numbers.
These objectives will help students develop a strong foundation for future years of learning math.
Helping Your Child With Third Grade Math
There are several ways to help your child master third-grade math concepts. First, you can create a regular study schedule that includes daily math practice. You can also integrate math into everyday activities such as cooking, grocery shopping, and playing games. Utilizing educational websites and math apps can also help your child develop problem-solving skills and improve their math performance. The provision of interactive math activities, math worksheets, and games makes learning fun and engaging. Materials such as games, activities, worksheets, websites, and academies help students to:
- Develop their auditory, visual, and kinesthetic skills
- Increase student engagement
- Build a sense of community in the classroom
- Improve self-efficacy
“The essence of mathematics is not to make simple things complicated, but to make complicated things simple.” – S. Gudder
Math Is All Around Us!
Mathematics is a fundamental aspect of our daily routine, whether it’s a trip to the supermarket or playing in the park. It is crucial for us as parents and educators to instill a love for math and its practical significance in everyday life. By incorporating math into everyday activities and introducing mathematical concepts early on, we can equip our children with critical thinking and problem-solving skills that will benefit them in the future. Alarming statistics reveal that just 40% of third-grade students in the US are proficient in math. Therefore, it is essential for children to master critical third-grade math concepts, such as multiplication, division, fractions, and geometry, as they serve as the building blocks for future mathematical learning.
Related Reading: Best Classroom Math Games
Make Your Child a Math Genius!

Math for 3rd graders is essential and sets the foundation for future math learning. By incorporating math into everyday activities, utilizing educational websites and math apps, and helping children develop an appreciation for the subject, we can help them develop the critical thinking and problem-solving skills they need to succeed. Let’s start by setting clear objectives and beginning the journey towards math proficiency today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the most important math concepts kids learn in 3rd grade?
The most important math concepts kids learn in 3rd grade include multiplication and division, fractions, geometry, measurement, and data analysis.
Why are multiplication and division important in 3rd-grade math?
Multiplication and division are important concepts in 3rd-grade math because they help children understand the relationships between numbers and develop problem-solving skills.
What is the significance of fractions in 3rd-grade math?
Fractions are a significant part of 3rd-grade math because they help children understand the concept of parts of a whole and lay the foundation for more complex math concepts in later grades.
What is geometry, and why is it important in 3rd-grade math?
Geometry is the study of shapes and their properties, and it’s important in 3rd-grade math because it helps children develop spatial reasoning skills and understand the world around them.
Why is data analysis important in 3rd-grade math?
Data analysis is an essential part of 3rd-grade math because it helps children learn how to collect, organize, and interpret data, a crucial skill in many fields and everyday life.