- Multimodal Learning Overview
- 4 Types of Multimodal Learning
- 4 Benefits of Multi-Modal Learning for kids
- 3 Strategies for Implementing Multi-Modal Learning
- Strategies for Visual Learners
- Strategies for Auditory Learners
- Strategies for Kinesthetic Learners
- 4 Examples of Multi-Modal Teaching
- Multi-Modal Learning in the Classroom
Multimodal learning means a way of teaching that uses different methods to help people learn. Instead of just listening to a lecture, students might also see things, read, write, or do activities. This is important because not everyone learns the same way. Some people remember things better when they see pictures, while others like to listen or move around while they learn.
Math & ELA | PreK To Grade 5
Kids see fun.
You see real learning outcomes.
Watch your kids fall in love with math & reading through our scientifically designed curriculum.
Parents, try for free Teachers, use for free
It’s important to use multimodal learning in today’s educational scenario. It helps make sure that all students have the chance to do well, no matter what their favorite way of learning is.
In this blog, we will discuss multimodal learning in depth, and it’s real-world applications that can benefit educators and learners in their academic journeys.
Interested in bringing multimodal learning to your classroom? Discover innovative tools and resources with SplashLearn.
Multimodal Learning Overview
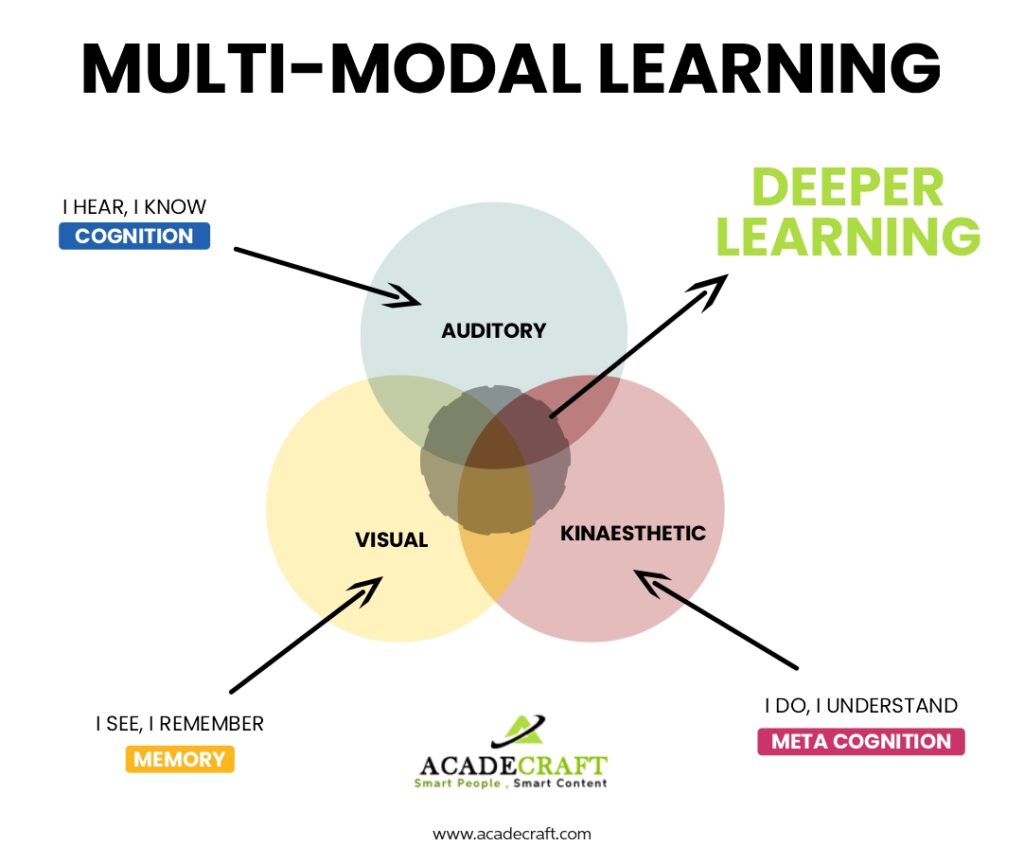
Multimodal learning is an educational approach that integrates various methods of learning, such as visual, auditory, and hands-on activities, to cater to the unique learning styles of each student. This approach is rooted in the cognitive theory that suggests the brain’s multiple ‘channels’ for processing information are more effectively stimulated when information is presented in diverse modes.
The components of multimodal learning encompass visual elements like charts and videos, auditory materials including lectures and podcasts, and reading, writing, and kinesthetic experiences involving movement and touch. Combining these elements, the multimodal approach addresses the wide range of learning style preferences. Crucially, multimodal learning is essential in catering to diverse learning needs, providing various ways for students to engage with content. It recognizes that each student has a distinct combination of strengths and preferences in learning, offering multiple pathways to understanding and accommodating all learners.
4 Types of Multimodal Learning
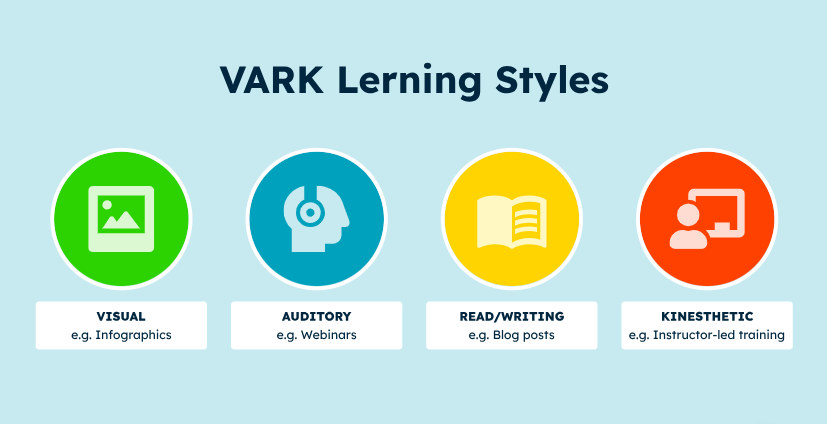
A. Visual Learning
Visual learning involves using images, maps, graphs, and other visual aids to help students see and understand concepts and ideas. It’s about showing rather than just telling.
Related Reading: Effective Ways To Teach Visual Learners
B. Auditory Learning
This type of learning focuses on listening. Auditory learners benefit from lectures, discussions, and listening to audio recordings or music. It’s all about hearing the information.
C. Reading/Writing Learning
Reading/writing learners engage with text-based materials. They learn best by reading texts and writing notes. This method relies heavily on the written word for learning and expressing ideas.
D. Kinesthetic Learning
Kinesthetic learning is a hands-on approach. It involves movement and physical activities to learn. Kinesthetic learners do best by touching, building, moving, or drawing what they learn.
4 Benefits of Multi-Modal Learning for kids
- Enhanced Engagement and Retention: Multimodal teaching uses different information presentation methods to boost student engagement. Students who are more engaged pay better attention and remember the material longer. For example, a student might watch a video about a historical event, discuss it, and act it out, which helps lock in the memory.
- Catering to Individual Learning Preferences: Every student has a way of learning that works best for them. Multi-modal learning taps into this by offering various options so each student can learn in the way they find easiest. This personalized approach means that all students can follow along and understand the lessons in their way.
- Improved Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills: When students are exposed to information in different forms, they learn to look at problems from different angles. This can lead to better critical thinking because they’re not just memorizing facts; they’re learning how to use that information in various situations, which is a key part of solving problems.
- Preparation for Real-World Challenges: The real world doesn’t stick to one way of presenting information. Using multi-modal learning, students prepare for real-life challenges where they must use different skills to understand and respond to the world around them. This kind of learning teaches them to adapt and use whatever resources they have to figure things out.
3 Strategies for Implementing Multi-Modal Learning
1. Understanding the Multimodal Approach: To use multimodal learning, it’s important first to understand that it combines different ways of learning. This means recognizing that some students prefer visuals, others like reading and writing, and some need to be active to learn best.
2. Integrating Various Learning Modes in Lesson Plans: When planning lessons, include activities that appeal to all learning styles. For example, a science lesson could start with a short video (visual), followed by a lecture (auditory), then reading an article (reading/writing), and finally experimenting (kinesthetic).
3. Balancing the Use of Different Modes to Enhance Learning: It’s key not to overuse one learning mode. Balance is important. Ensure that no one way of learning overshadows the others so all students have an equal chance to understand and participate.
Implementing multimodal learning is easier with the right tools. SplashLearn offers a variety of resources tailored to every learning style. Explore more and enrich your teaching methods.
Strategies for Visual Learners

5 Strategies for Teachers
- Use of Visual Aids: Teachers can use posters, models, and flashcards to make lessons more interesting and easily remember.
- Incorporating Diagrams and Charts: Diagrams and charts can help break down complex information into clear, visual pieces.
- Implementing Mind Mapping Techniques: Mind maps can help students understand and remember relationships between concepts.
- Utilizing Videos and Animations: Videos and animations can bring content to life and make abstract ideas more concrete.
- Encouraging Visual Note-Taking: Teachers can show students how to use sketches and symbols in their notes to help them visualize the material.
Related Reading: Best Virtual Learning Tools for Kids and Teachers
5 Strategies for Students
- Creating Visual Study Guides: Students can make their visual aids like charts or concept maps to summarize information.
- Organizing Information Visually: Using bullet points, lists, and spatial organization on the page can help review and recall information.
- Engaging with Infographics: Infographics combine images and data, which can be a powerful tool for visual learners to grasp complex information.
- Visualizing Data and Concepts: Turning numbers and ideas into graphs or visual representations can make them easier to understand.
Using Color Coding for Notes: Different colors can help highlight key points and organize notes by topic or importance.
Visual aids can significantly enhance learning. SplashLearn’s interactive and visually engaging content is perfect for your classroom.
Strategies for Auditory Learners

5 Strategies for Teachers
- Incorporating Discussions and Debates: Engage students in classroom discussions and debates to help them process information through listening and speaking.
- Using Music and Rhymes as Mnemonic Devices: Integrate music and rhymes into lessons to make memorization of facts more enjoyable and effective.
- Employing Audio Recordings and Podcasts: Provide lectures in audio format or recommend educational podcasts that reinforce lesson content.
- Reading Aloud and Verbal Explanations: Regularly read material aloud and give verbal explanations to reinforce key concepts.
- Encouraging Oral Presentations: Have students present their work to the class to strengthen their understanding and verbal communication skills.
5 Strategies for Students
- Participating Actively in Discussions: Join in class discussions to better absorb and understand the material.
- Listening to Educational Audio Material: Use audiobooks and educational podcasts as study aids to reinforce learning.
- Recording and Reviewing Lectures: Record lectures to replay and listen to the information multiple times.
- Engaging in Peer Teaching: Explain concepts to classmates to improve understanding and retention of the material.
- Utilizing Rhythmic Patterns for Memorization: Use rhythmic patterns or put information to a tune to help remember facts and details.
Related Reading: Best Audiobooks for Kindergarteners and Preschoolers
Strategies for Kinesthetic Learners

5 Strategies for Teachers
- Incorporating Hands-On Activities: Introduce activities where students can manipulate materials, which is a key learning method for kinesthetic learners.
- Using Real-Life Simulations and Role-Plays: Simulate real-world scenarios in the classroom to make learning more tangible and memorable.
- Organizing Field Trips and Experiential Learning: Take learning outside the classroom to provide real-life experiences that resonate with kinesthetic learners.
- Implementing Lab Experiments and Demonstrations: Conduct experiments and live demonstrations to illustrate concepts actively.
- Encouraging Movement and Gestures in Learning: Allow students to use body movements and gestures to express their understanding of the material.
5 Strategies for Students
- Engaging in Active Experimentation: Dive into learning by trying out things practically, which is one of the effective learning modalities for kinesthetic learners.
- Building Models and Prototypes: Create physical models to understand abstract concepts better.
- Participating in Sports and Physical Education: Use the physical activity of sports as a way to connect with learning topics.
- Using Body Mapping for Learning: Map out ideas and concepts using the body as a guide to aid memory and understanding.
- Applying Learning in Practical Settings: Look for opportunities to apply classroom knowledge in real-world situations, enhancing the learning experience.
4 Examples of Multi-Modal Teaching
1. Educational Games
Educational games are multimodal examples that combine visual, auditory, and kinesthetic elements to create a dynamic learning experience. They can help students learn new concepts and reinforce existing knowledge in an interactive way.
Experience the power of learning through play with educational games. Designed to captivate and educate, our games enhance classroom learning.
2. Group Projects
Group projects encourage students to collaborate and learn from each other, incorporating various examples of learning experiences. They often involve research, discussion, and hands-on activities, catering to different learning styles.
3. Case-Based Learning
Case-based learning presents real-world scenarios for students to work through, integrating multiple learning modalities. This approach helps students apply theoretical knowledge to practical problems.
4. Personalized Journal Entries
Personalized journal entries allow students to reflect on their learning using written words and visual elements. This method supports reading/writing learners while giving space for visual expression.
Multi-Modal Learning in the Classroom
A. Integrating Multi-Modal Learning into a Typical Classroom Setting
Integrating multimodal learning strategies into a classroom means using various teaching methods to reach every student. This could look like a mix of lectures, visual aids, group work, and hands-on activities throughout the week to cover a single topic from multiple angles.
B. The Role of Technology in Supporting Multi-Modal Instruction
Technology is a key player in multimodal instruction. It offers tools like educational software, online resources, and interactive whiteboards, making it easier to bring multimodal learning means into the classroom. These technologies can cater to different learning preferences and make lessons more engaging.
C. Adapting to Different Learning Styles with Technology
Technology makes it possible to adapt teaching methods to various learning styles quickly. For example, digital platforms can provide interactive exercises for kinesthetic learners, podcasts for auditory learners, infographics for visual learners, and blogs or forums for reading/writing learners.
We hope this guide helps you understand how different learning methods can improve the classroom for everyone. By trying these ideas, teachers can help students learn the best way.
Related Reading: What Is “Inquiry-Based Learning”?: Types, Benefits, Examples
Frequently Asked Questions
Can multimodal learning help with student engagement?
Yes, multimodal learning can increase student engagement by using different activities that make lessons interesting and help students connect with the material in various ways.
How can a teacher find out which learning style each student prefers?
Teachers can observe how students interact with different activities, ask them directly, or have them take learning style quizzes to understand their preferences.
Are there any challenges to implementing multimodal learning?
Challenges can include limited resources, large class sizes, or finding the right balance of activities, but with creativity and planning, these can be managed effectively.
What is an example of multimodal machine learning?
An example of multimodal machine learning is a recommendation system that suggests products based on a combination of text reviews, images of the products, and user interaction data. This system learns from different types of data (text, image, and click-through rates) to improve its accuracy in predicting what a user might like.
























