Remember when your kids first made their bed or threw a tantrum over vegetables? How did you react—praise, scold, or ignore? Do you think about the impact of your actions? For decades, parents and teachers have used positive and negative reinforcement to shape behavior. In this blog, we’ll explore negative reinforcement, its nuances, and how to use it effectively to foster better behavior.
Math & ELA | PreK To Grade 5
Kids see fun.
You see real learning outcomes.
Watch your kids fall in love with math & reading through our scientifically designed curriculum.
Parents, try for free Teachers, use for free
What is Negative Reinforcement?
Negative reinforcement occurs when something unpleasant or uncomfortable is removed or taken away in order to increase the likelihood of the desired behavior. Kids want to avoid the nagging, so they do what needs to be done. Thus, taking away something unpleasant, in this case, nagging, results in the desired behavior.
10 Examples of Negative Reinforcement
5 Negative Reinforcement Examples at Home
1. Turning off a loud music player – When a child completes their morning routine on time, a parent can turn off an intentionally loud music player, making mornings more pleasant.
2. Stopping the timer noise – A timer is set when a child begins cleaning their room; the timer is turned off once they finish, removing the stressful noise and encouraging quicker clean-up.
3. Skipping a less favored chore – If a child helps with cooking dinner, they can skip doing the dishes for that evening, encouraging them to take part in cooking activities.
4. Removing an uncomfortable clothing item – When a child communicates that a clothing tag is itchy, removing it teaches them that expressing discomfort can lead to more comfort.
5. No additional chores – On days when a child finishes their homework before dinner, they are exempt from additional evening chores, motivating them to complete their schoolwork promptly.
5 Examples of Negative Reinforcement in the Classroom
1. Turning off loud noise – Once all students are quietly seated and ready, the teacher turns off a loud sound (like a bell or music), which had been used to signal the need for order.
2. Ending less preferred activities – If the class completes all their assignments on time, the teacher can cancel a scheduled quiz, promoting timely submission of assignments.
3. Removing restrictions – Once students have shown they can work quietly on their own, a teacher might remove a “silent work” rule, allowing for quiet discussion, thus promoting responsible behavior.
4. Skipping additional tasks – Students who consistently perform well in weekly assessments may be allowed to skip the usual end-of-week review sessions, rewarding their consistent effort and understanding.
5. Easing up on strict seating – If students demonstrate they can work effectively in a less rigid seating arrangement, the teacher can allow them to choose their seats as a way to encourage continued cooperation and focus.
Reinforcement Vs Punishment
Primarily, there are two types of reinforcement:
- Positive reinforcement: adding a factor to increase the likelihood of the desired behavior.
- Negative reinforcement: removing a factor to increase the likelihood of the desired behavior.
The main point to be noted is that in both strategies, the goal is to increase the likelihood of desired behavior.
However, there are certain misconceptions among parents and teachers that negative reinforcement means punishment. In reality, that is not the case. Let’s understand the difference between the two.
Related Reading: Learning Styles That Make Learning Easy-Peasy For Kids
Negative Reinforcement Vs Punishment
The most obvious difference between punishment and negative reinforcement lies in the fact that punishment, whether positive or negative, aims at decreasing or weakening a behavior. Whereas reinforcement, whether positive or negative, aims at strengthening the behavior. Now, this may be done by either adding or removing a factor.
Watch this video to understand the difference between negative reinforcement and punishment.
Let’s consider the following example for better understanding:
Jack is supposed to take his dog for a walk every morning. This morning he woke up late and was not able to take the dog for a walk. Because of this, his mother made him do other chores around the house in addition to taking the dog for a walk in the evening.
This is an example of punishment because his mother punished him for not taking the dog for a walk in the morning. The mother’s objective was to weaken the irresponsible behavior portrayed by Jack.

But what different approach could Jack’s mother have taken to apply negative reinforcement? She could have removed an existing obligation: If Jack managed to wake up early for a week and take the dog for a walk, she could cancel his weekend chores. This removal of an unpleasant task would encourage Jack to maintain his punctual morning routine.
Another way to distinguish between negative reinforcement and punishment is to note whether an unwanted outcome is being added as a consequence of behavior. If it is being added, then it is an example of punishment. But if something is being removed in order to avoid unwanted behavior, then it is an example of negative reinforcement.
In addition, punishment tries to make the unwanted behavior stop, whereas negative reinforcement tries to make the wanted behavior more likely to occur.
Whether positive or negative, research has time and again proven that reinforcement is more effective in molding behaviors than punishment, as the latter leads to more negative outcomes and impacts.
Positive Reinforcement Vs Negative Reinforcement
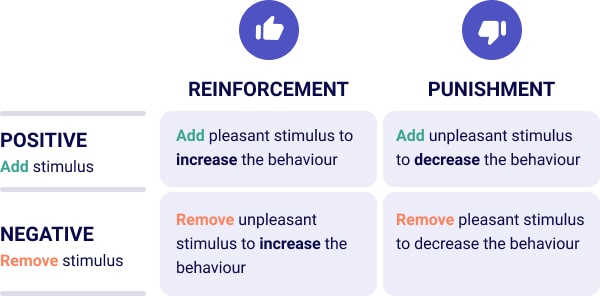
Here are the main difference between positive and negative reinforcement:
| Aspect | Positive Reinforcement | Negative Reinforcement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adding a pleasant stimulus to increase the likelihood of a behavior being repeated. | Removing an unpleasant stimulus to increase the likelihood of a behavior being repeated. |
| Purpose | To encourage and strengthen positive behavior by providing a reward. | To encourage and strengthen behavior by removing an undesirable condition or feeling. |
| Example in Use | A teacher gives a student a sticker for completing their homework on time. | A teacher stops playing a loud noise once all students are seated and quiet. |
| Impact on Behavior | Makes the desired behavior more likely to occur by associating it with positive consequences. | Makes the desired behavior more likely to occur by eliminating negative consequences. |
| Typical Application | Used to motivate individuals by rewarding them directly for specific actions or behaviors. | Used to alleviate discomfort or irritation, leading to an increase in the desired behavior. |
| Psychological Effect | Creates a feeling of reward and pleasure, reinforcing the behavior. | Reduces or eliminates discomfort, making the relief itself a reinforcer of the behavior. |
Negative Reinforcement vs Negative Punishment
| Aspect | Negative Reinforcement | Negative Punishment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Removing an unpleasant stimulus to increase the likelihood of a behavior. | Removing a pleasant stimulus to decrease the likelihood of a behavior. |
| Purpose | Aims to increase the likelihood of a desired behavior. | Aims to decrease the likelihood of an undesired behavior. |
| When to Use | Useful for encouraging and strengthening positive behaviors. | Useful for discouraging and reducing negative behaviors. |
| Example Situation | A child behaves well in class to avoid the teacher’s scolding. | A child misbehaves and has their favorite toy taken away. |
| Effect on Behavior | The removal of the unpleasant stimulus (scolding) increases good behavior. | The removal of the pleasant stimulus (toy) decreases misbehavior. |
| Desired Outcome | Increase in desired behavior. | Decrease in undesired behavior. |
| Strategic Application | Employed to enhance and foster positive behavior by alleviating discomfort. | Employed to curb and prevent negative behavior by removing privileges or rewards. |
Is Negative Reinforcement Bad?
Using negative reinforcement as a behavior management tool isn’t necessarily bad.
The word ‘negative’ refers to the act of taking something away, like a minus sign in a math equation, which of course, has no negative effect on the child or the person.
Moreover, the thing or factor that is taken away is something that the child or the person finds uncomfortable or unpleasant, so its removal results in a desirable outcome, thus turning it into a favorable condition. So, negative reinforcement is not a negative thing, but it’s about removing the ‘negative’ thing.
Conclusion
The question of “is negative reinforcement effective” often arises in discussions of behavioral strategies. Indeed, it proves to be an effective tool for increasing desirable behaviors by removing negative stimuli. This approach not only fosters positive changes but also emphasizes the importance of understanding and applying psychological principles wisely in both educational and home environments.
Related Reading: Best Parenting Strategies For Positive Discipline in Kids
























