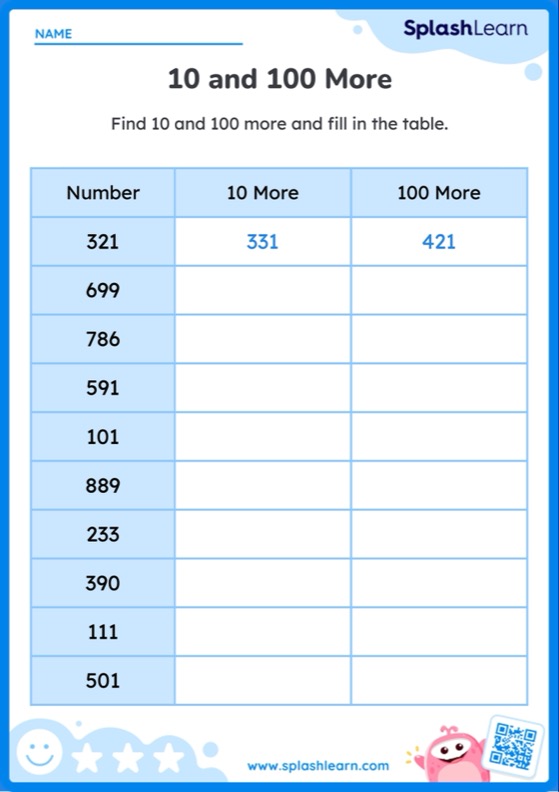
Definition of Equivalent
The meaning of ‘equivalent’ generally refers to two numbers, expressions, or quantities with the same value. There are many ways to express an equivalent quantity – it can be denoted either by a bar or an equivalent symbol. Children find this topic very interesting for several reasons as they can relate to it in their daily lives.
The equivalent can also mean some common or logical equivalence between different values or quantities. Equivalence is similar but not the same as equality.
Recommended Games
What Is the Meaning of Equivalent in Math?
There are two ways in which one can define an equivalent in math. This is because the term equivalent in mathematical theory is a notion that has multiple meanings. Equivalent means that different terms and expressions with a similar value are considered equal in mathematical form.
Equal Vs Equivalent
In math, equivalent is different from equal. Equal means same in all aspects, whereas equivalent means similar but not identical.
For example, 2 is said to be equal to 2 but equivalent to 1 + 1.
In simple words we can say that two things or quantities are equal when they are exactly the same like ½ is equal to ½ but ½ is equivalent to 2/4 as they represent the same value.
Equivalent Expressions
Two mathematical expressions are said to be equivalent if they yield the same result upon solving them.
For example, let’s solve the following numerical expressions:
25 × 5 = 125
Also, 10$^{2}$ + 5$^{2}$ = 100 + 25 = 125
Thus, the above two expressions are equivalent and can be written as:
25 × 5 = 10$^{2}$ + 5$^{2}$
Similarly, the two math expressions 2 × (10 – 8) and 4$^{2}$ ÷ 4 are also equivalent as both can be simplified to 4.
Equivalent Fractions
Two fractions are equivalent if the value, proportion, or quantity they represent is the same. Equivalent fractions can have different numerators and denominators.
For example: $\frac{1}{2}$ = $\frac{2}{4}$ = $\frac{3}{6}$ = $\frac{4}{8}$

Equivalent Ratios
Equivalent ratios are those which can express a similar or the same relationship between numbers or values.
They are similar in ratios and identical in value. These ratios can be multiplied or divided by their common factors, which can help simplify them. Equivalent ratios have different numbers in different forms, but their relationship is reflected only by their final value.
For example, 1:2 and 2:4 are equivalent ratios.
Application
The use of the equivalent symbol (as three bars) is frequently used in Unicode programming for computers, as well as in Boolean algebra. Venn diagrams use the concept of logical equivalence to establish the relationship between two algebraic expressions and functions. The concept of equivalence is also used in explaining the structural similarity between the chemical compounds.
Recommended Worksheets
Solved Examples
Example 1: Two fractions, $\frac{3}{5}$ and $\frac{6}{x}$, are equivalent. Find the value of x.
Solution: Given, $\frac{3}{5}$ = $\frac{6}{x}$
We know that equivalent fractions can be generated by multiplying the numerator and the denominator by the same number. So $\frac{3}{5}$ = $\frac{6}{10}$.
Hence, x = 10.
Example 2: Check whether 7 × 6 + 66 ÷ 11 – 5 × 2 is equivalent to 7 × 3 + 24 ÷ 2 + 9 × 3 or not.
Solution: In order to verify the equivalence of both the expressions, solve the and find the final values.
7 × 6 + 66 ÷ 11 – 5 × 2
= 42 + 6 – 10
= 38
7 × 3 + 24 ÷ 2 + 9 × 3
= 21 + 12 + 27
= 60
38 ≠ 60
So, the given expressions are not equivalent to each other.
Example 3: Are $\frac{4}{5}$ and $\frac{16}{20}$ equivalent fractions?
Solution:
$\frac{4\times 4}{5\times 4}$ = $\frac{16}{20}$
If we multiply numerator and denominator of $\frac{4}{5}$ by 4, we get $\frac{16}{20}$.
So, the given fractions are equivalent.
Practice Problems
Equivalent
Choose the fractions equivalent to $\frac{5}{3}$ from the list of fractions that are shown below.
$\frac{5\times 2}{3\times 2}$ = $\frac{10}{6}$
Choose a fraction equivalent to ‘five-sixths’
$\frac{5\times 5}{6\times 5}$ = $\frac{25}{30}$
Two fractions $\frac{4}{15}$ and $\frac{12}{x}$ are equivalent. Find the value of x.
$\frac{4\times 3}{15\times 3}$ = $\frac{12}{45}$
Conclusion
We have learned about the equivalent and its properties and properties with different examples. We have also solved a few problems that have helped us grasp the concept of equivalent. Hopefully, this will help the kids master the concept to solve different mathematical problems.
Teaching math concepts can be challenging, especially when the students are young kids. So, to make parents’ and teachers’ lives easy, SplashLearn has brought some courses specifically designed for students from K-8. After all, it should be fun to learn!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some examples of equivalent values?
Some examples of equivalent values would be fractions like $\frac{1}{2}$ and $\frac{2}{4}$. They are both simplified at 0.5 each. An example of an equivalent ratio would be 1:5 and 2:10, as, after simplification, they would both have the same value, making them equivalent.
Are equivalent fractions and equivalent ratios the same?
Yes, equivalent fractions are the same as they are two different ways of representing the same concept. Equivalent ratios, sometimes known as equivalent fractions, are ratios that have the same proportion to each other when put in simplest form.
How do we find equivalent fractions?
To find equiavlent fractions, we multiply the numerator and denominator by the same number.
What are some real-life examples of equivalent fractions?
For example, let’s say we are making a recipe that requires 1/2 cup of butter. But we only have 1/4 cups in the kitchen. Can we still make the recipe? Yes! Because 1/2 is equivalent to 2/4. So, we can use two 1/4 cups of butter instead of one 1/2 cup.