Cross Multiplication: Introduction
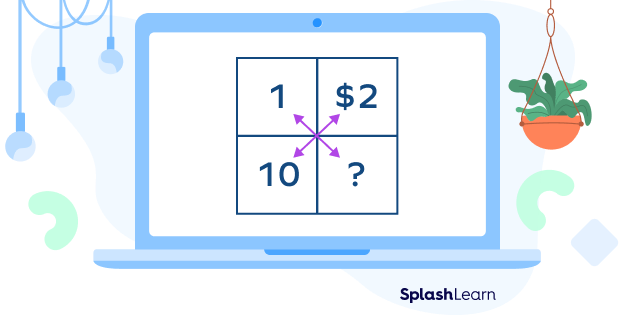
We commonly use the cross multiplication method to find unknown values in any algebraic equation. Let’s look at these everyday math questions. If one candy bar costs $\$$2, how much would 10 such candy bars cost?
Cross multiplication, as the name suggests, refers to multiplying numbers placed at cross positions.
We cross multiply fractions $\frac{1}{10}$ and $\frac{2}{?}$.
$? \times 1= $\$$10$ $\times 2$
$? =$ $\$$20
So, 10 candy bars would cost $\$$20.
Let’s learn more about this method and its applications.
Recommended Games
What Is Cross Multiplication?
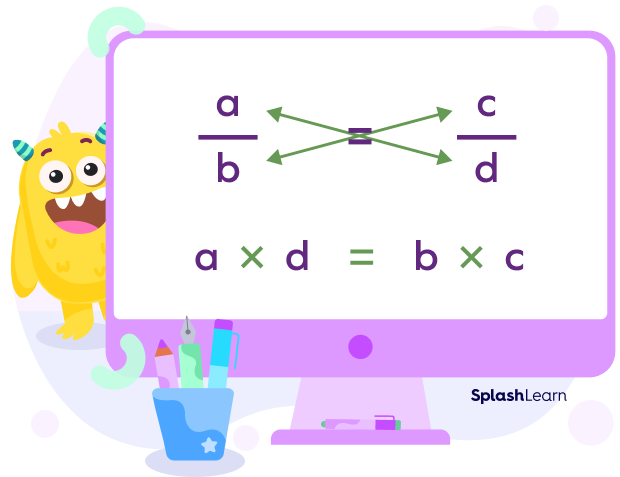
For any algebraic equation like $\frac{a}{b}=\frac{c}{d}$, the cross multiplication method uses the following formula:
$a\times d = b\times c$
To cross multiply fractions, we multiply the numerator of the first fraction with the denominator of the second fraction and the numerator of the second fraction with the denominator of the first fraction.
Cross multiplication can be used to compare fractions, to add or subtract unlike fractions, to find unknown value in an expression, and to compare ratios.
Recommended Worksheets
How to Cross Multiply Fractions?
Let’s understand how to cross multiply fractions using an example.
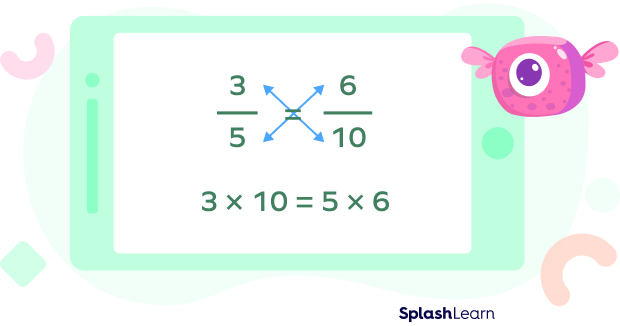
We know that $\frac{3}{4} = \frac{6}{8}$
Cross multiply fractions $\frac{3}{4}$ and $\frac{6}{8}$.
Multiply the numerator of the first fraction with the denominator of the second fraction.
Multiply the numerator of the second fraction with the denominator of the first fraction.
We get
$3\times8=24$
$6\times4=24$
So, by cross-multiplying fractions $\frac{a}{b} = \frac{c}{d}$ , we get $a\times d = b\times c$
Cross Multiply Fractions to Compare Unlike Fractions
We just learnt how to cross multiply fractions. When do you cross multiply fractions? Unlike fractions can be compared by cross multiplying. Unlike fractions are fractions that have different denominators.
Example:
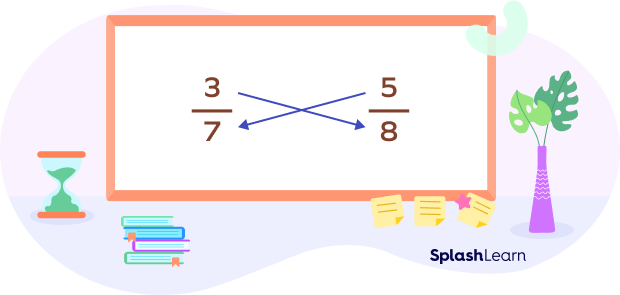
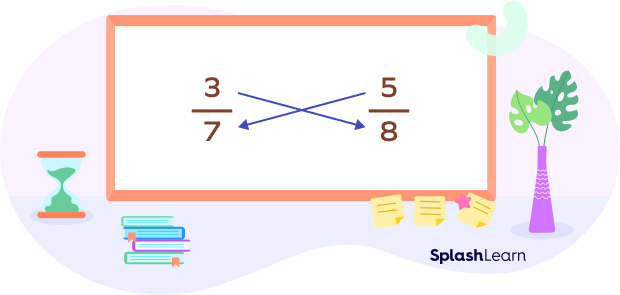
Compare $\frac{3}{7}$ and $\frac{5}{8}$ using cross-multiplication.
To compare two fractions with different denominators, we make their denominators the same.
We do it by changing the denominators to the product of both denominators.
So, the denominator of both the fractions becomes $7 \times 8 = 56$
Now, we cross multiply fractions to find the numerators.
- First, we multiply the numerator of the first fraction with the denominator of the second fraction.
$3 \times 8 = 24$
So, the first fraction becomes: $\frac{24}{56}$
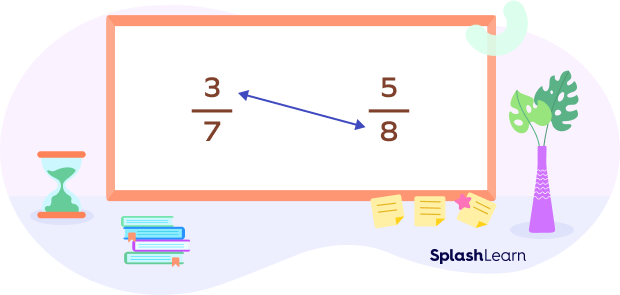
- Next, we multiply the second fraction’s numerator by the first fraction’s denominator.
$5 \times 7 = 35$
So, the second fraction becomes: $\frac{35}{56}$
Since $\frac{24}{56} \lt \frac{35}{56}$ , we can say that $\frac{3}{7} \lt \frac{5}{8}$.
Cross Multiplication to Compare Ratios
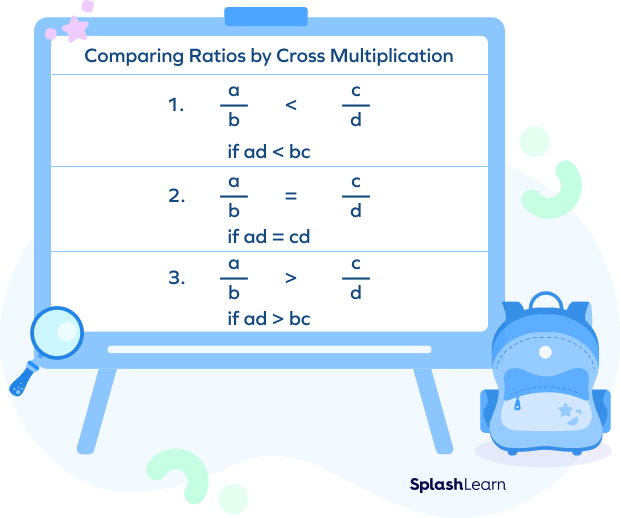
If two ratios are equal, i.e., $\frac{a}{b} = \frac{c}{d}$, (where b and d are not equal to zero), then the product after cross multiplication is also equal.
- $\frac{a}{b} \lt \frac{c}{d}$ if $a\times d \lt b\times c$.
Example: $\frac{1}{2} \lt \frac{3}{4}$ since $4 \lt 6$.
- $\frac{a}{b} \gt \frac{c}{d}$ if $a \times d \gt b \times c$.
Example: $\frac{1}{10} \gt \frac{1}{100}$ since $100 \gt 10$.
We can use cross-multiplication to find the value of a variable in an equation involving ratios. Let us understand this better with an example.
Example: If 8 candle-stands cost $\$$40. How much will 12 such candle-stands cost?
Cost of 8 candle-stands = $\$$40
Cost of 1 candle-stands $= \frac{40}{8}$ …………(i)
Let the cost of 12 candle-stands be x.
Therefore, the cost of 1 candle-stands will be $\frac{x}{12}$. …………..(ii)
Equating (i) and (ii), we get
$\frac{40}{8} = \frac{x}{12}$
Cross multiply to get
$40 \times 12 = 8 \times x$
$\frac{480}{8}=$ x
x $=60$
Therefore, the cost of 12 candle-stands is $\$$60.
Cross Multiplication with One Variable
The cross multiplication method is mostly used to find the unknown variable in an equation. Let’s look at an example.
$\frac{4}{9} = \frac{x}{45}$
When we cross multiply:
$4 \times 45 = 180$ and $9 \times x = 9x$
Now, $9x = 180$
x$ = \frac{180}{9} = 20$
Therefore, we get $x = 20$
Solved Examples on Cross Multiplication
1. Compare the fractions 57 and 49 by cross multiplying.
Solution: When we cross multiply, we find,
$5 \times 9 = 45$ and $4 \times 7 = 28$
Since $45 \gt 28, 57$ is greater than 49.
2. Jimmy wants to find the value of x in the given equation. Can you help him?
$\frac{12}{15} = \frac{x}{10}$
Solution:
$\frac{12}{15} = \frac{x}{10}$ ( given)
On cross multiplying:
$12 \times 10 = 15 \times x$
$\frac{120}{15} =$ x
$8 =$ x
So, the value of x is 8.
3. Which is bigger, $\frac{7}{12}$ or $\frac{6}{11}$?
Solution:
When we cross multiply, we find
$7 \times 11 = 77$ and $6 \times 12 = 72$
As, $77 \gt 72$
Therefore, $\frac{7}{12} \gt \frac{6}{11}$.
Practice Problems on Cross Multiplication
Cross Multiply Fractions
If fractions $\frac{4}{8}$ and $\frac{5}{x}$ are equal, what’s the value of $x$?
Since the given fractions are equal, we can cross multiply and say that $4x= 8 \times 5 = 40$
Thus, x $=$ 10
If 4 cupcakes cost $\$$12. How much will 10 such cupcakes cost?
The cost of 4 cupcakes is $\$$12.
Let the cost of 10 cupcakes be the variable x. When we frame it as an equation, we have:
$\frac{12}{4} = \frac{x}{10}$
When we cross multiply, we get
$12 \times 10 = 4 \times x$
$\frac{120}{4} = x$
$30 = x$
Therefore, the cost of 10 cupcakes is $\$$30.
What is the value of x if $\frac{9}{11} = \frac{x}{33}$.
$\frac{9}{11}= \frac{x}{33}$
On cross multiplying:
$9 \times 33 = 11\times x$
$\frac{297}{11} = x$
$x = 27$
So, the value of $x$ is 27.
Frequently Asked Questions on Cross Multiplication
When do we use cross multiplication?
We use the cross multiplication method for the following:
- The process of cross multiplying is used to compare both fractions and ratios. Using this, we can gauge if they are equal, greater, or lesser.
- It is also used in finding the value of variables in an expression.
2. How is cross multiplication used to find the value of a variable?
Cross multiplication is done on the numerators and denominators of the fractions, which are present on both sides of the equation. Next, we solve the equation to find the unknown variable
Do we use cross multiply fractions?
No, we do not cross multiply when multiplying fractions. To multiply fractions, we multiply the numerators with numerators and denominators.




































