What Is a Common Denominator in Math?
A common denominator is a common multiple of the denominators of two or more fractions.
Example:
| $\frac{2}{5}, \frac{3}{5}$ | $\frac{18}{21}, \frac{9}{21}, \frac{3}{21}$ | $\frac{6}{7}, \frac{3}{5}, \frac{1}{3}$ |
| 5 is a common denominator. | 21 is a common denominator. | The fractions have different denominators. |
In simple words, when the denominators of two or more fractions are the same, then the denominator is known as the common denominator. Fractions having the same denominator are called “like fractions.”
Recommended Games
Why Is the Common Denominator Important?
Performing any arithmetic operation, such as addition or subtraction on two or more fractions, is possible only if the denominators of both fractions are the same.
This is because we can define a fraction only when the whole is divided into the equal number of parts. The denominator represents the total number of equal parts a whole is divided into.
What Is a Fraction?
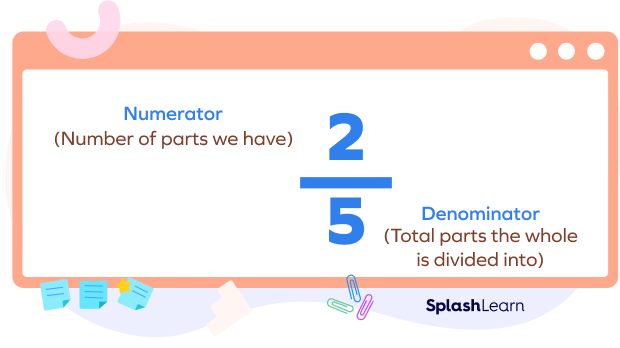
A fraction represents parts of a whole where the whole is divided into equal parts. In a fraction, pq, the p is the numerator that tells us about the number of parts we have taken; and q is the denominator that defines the total parts the whole object is divided into.
Recommended Worksheets
Common Denominator: Definition
A common denominator of two or more fractions is the shared multiple of their denominators.
Example: The common denominators of $\frac{2}{3}$ and $\frac{5}{7}$ are 21, 42, 63, 84, etc. It means that both the fractions have equivalent fractions with denominators 21, 42, 63, 84, etc.
$\frac{2}{3} = \frac{14}{21} = \frac{28}{42} = \frac{42}{63}$
$\frac{5}{7} = \frac{15}{21} = \frac{30}{42} = \frac{45}{63}$
What Is the Least Common Denominator?
The Least Common Denominator (LCD) of two or more fractions is the LCM of their denominators. It is the smallest multiple shared between the denominators of the given fractions.
How to Find Common Denominator
When two or more fractions have different denominators, they are called “unlike fractions.”
To add or subtract unlike fractions (fractions with different denominators), the first step is to convert them into like fractions (fractions with same denominators) by finding the common denominator.
There are different ways for finding the common denominators. Finding the LCD of two fractions is the easiest way to convert unlike fractions into like fractions.
LCM Method
In this method, we find the LCD of the two fractions. We list the multiples of the denominators and identify the LCM.
Example: $\frac{5}{8}$ and $\frac{11}{12}$.
Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48,…
Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48,…
Common multiples of 8 and 12: 24, 48, …
LCM of denominators = 24
LCD of fractions = 24
Now, we will find the equivalent fractions of $\frac{5}{8}$ and $\frac{11}{12}$ such that their new denominators are 24.
$\frac{5}{8} = \frac{5 \times 3}{8 \times 3} = \frac{15}{24}$
$\frac{11}{12} = \frac{11 \times 2}{12 \times 2} =\frac{22}{24}$
Note that 24 is the LCD (least common denominator).
The common denominators are 24, 48, 72, etc.
Cross Multiplication Method
This is a very straightforward method. It can be used for any type of fractions.
To find the common denominator of two fractions $\frac{a}{b}$ and $\frac{c}{d}$, we multiply each fraction (both numerator and denominator) by the denominator of the other fraction.
$\frac{a}{b} = \frac{a \times d}{b \times d} = \frac{ad}{bd}$ and $\frac{c}{d} = \frac{c \times b}{d \times b} = \frac{bc}{bd}$
If you want to add or subtract two fractions ab and cd using the cross multiplication method, we can write
- $\frac{a}{b} + \frac{c}{d} = \frac{ad + bc}{bd}$
- $\frac{a}{b} – \frac{c}{d} = \frac{ad – bc}{bd}$
Example: $\frac{3}{7} + \frac{5}{4}$
$= \frac{3 \times 4}{7 \times 4} + \frac{5 \times 7}{4 \times 7}$
$= \frac{(3 \times 4) + (5 \times 7)}{7 \times 4}$
$= \frac{12 + 35}{28}$
$= \frac{47}{28}$
Finding Common Denominator when HCF of Denominators is equal to 1
If the HCF of denominators is 1, then the LCD of fractions is the product of the denominators.
Example: $\frac{1}{9}$ and $\frac{4}{7}$.
HCF(9, 7) = 1
LCM(9, 7) = 9 ✕ 7 = 63
LCD( $\frac{1}{9} , \frac{4}{7}$) = 63
Converting the fractions $\frac{1}{9}$ and $\frac{4}{7}$ into like fractions with common denominator 63, we get
$\frac{1}{9} = \frac{1 ✕ 7}{9 ✕ 7} = \frac{7}{63}$
and
$\frac{4}{7} = \frac{4 ✕ 9}{7 ✕ 9} = \frac{36}{63}$
Applications of Common Denominator
- For ordering fractions
Using the least common denominator, fractions can be arranged in ascending or descending order. For example, to arrange the following numbers in ascending order, we find their LCD.
$\frac{3}{5}, \frac{9}{20}, \frac{4}{6}$
| Multiples of 5 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | … |
| Multiples of 20 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 120 | 140 | 160 | 180 | 200 | 220 | 240 | … |
| Multiples of 6 | 6 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 42 | 48 | 54 | 60 | 66 | 72 | … |
The LCD of fractions is 60.
Thus fractions can be rewritten as: $\frac{36}{60}, \frac{27}{60}, \frac{40}{60}$
In ascending order, we get: $\frac{27}{60} \lt \frac{36}{60} \lt \frac{40}{60}$
Thus, $\frac{9}{20} \lt \frac{3}{5} \lt \frac{4}{6}$
In descending order, we get: $\frac{40}{60} \gt \frac{36}{60} \gt \frac{36}{60}$
Thus, $\frac{4}{6} \gt \frac{3}{5} \gt \frac{9}{20}$
- Adding and subtracting fractions
Using the least common denominator, fractions can be added and subtracted. For example, to arrange the following numbers in ascending order, we find their LCD.
Example: $\frac{5}{6} – \frac{9}{20}$
LCD(6, 20) = 60
$\frac{5 \times 10}{6 \times 10} = \frac{50}{60}$
$\frac{9 \times 3}{20 \times 3} = \frac{27}{60}$
We get
$\frac{50}{60} – \frac{27}{60} = \frac{13}{60}$
Facts about Common Denominators
- Finding a common denominator allows fractions to be rewritten as equivalent fractions with the same denominator.
- Common denominators make it easier to add, subtract, or compare unlike fractions.
- The product of the two denominators is always a common denominator of any two fractions.
- If the denominators are co-prime, the LCD of two fractions is the product of their denominators.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned about common denominators of fractions, methods to calculate the common denominator, and its applications. Let’s solve a few examples, and practice MCQs for revision.
Solved Examples on Common Denominator
1. Find the least common denominator of $\frac{2}{3}, \frac{1}{7}$, and $\frac{4}{5}$.
Solution:
The HCF of 3, 7, and 5 is 1.
Thus, LCM(3, 7, 5) = 3 × 5 × 7 = 105
Thus, LCD($\frac{2}{3}, \frac{1}{7}, \frac{4}{5}$) = 105
The common denominator $\frac{2}{3}, \frac{1}{7}$, and $\frac{4}{5}$ is 105.
2. Simplify using the cross multiplication method: $\frac{9}{4} – \frac{4}{3}$.
Solution:
$\frac{9}{4}$ and $\frac{4}{3}$ have different denominators.
Let’s find the common denominator.
Multiply both the numerator and denominator of $\frac{9}{4}$ by 3.
$\frac{9 \times 3}{4 \times 3} = \frac{27}{12}$
Multiply both the numerator and denominator of $\frac{4}{3}$ by 4.
$\frac{4 \times 4}{3 \times 4} = \frac{16}{12}$
Thus, we write
$\frac{9}{4} – \frac{4}{3} = \frac{27}{12} – \frac{16}{12} = \frac{11}{12}$
3. Find the least common denominator for $\frac{1}{6}$ and $\frac{1}{18}$? Rewrite these fractions with the common denominator of 54.
Solution:
Multiples of 6 = 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54, …
Multiples of 18 = 18, 36, 54, …
LCM (6, 18) = 18
Thus, 18 is the common denominator of $\frac{1}{6}$ and $\frac{1}{18}$.
We can write two more common denominators by finding the multiples of 18.
Let’s rewrite $\frac{1}{6}$ and $\frac{1}{18}$ with the common denominator of 54.
$\frac{1}{6} = \frac{1 \times 9}{6 \times 9} = \frac{9}{54}$
$\frac{1}{18} = \frac{1 \times 3}{18 \times 3} = \frac{3}{54}$
Practice Problems on Common Denominators
Common Denominator – Definition, Applications, Facts, Examples
Which of the following is correct?
LCD = LCM(6, 8) = 24
$\frac{1 \times 4}{6 \times 4} = \frac{4}{24}$ and $\frac{5 \times 3}{8 \times 3} = \frac{15}{24}$
$\frac{4}{24} \lt \frac{15}{24}$
Thus, $\frac{1}{6} \lt \frac{5}{8}$
The least common denominator of fractions is the
The LCD can be found by multiplying the denominators or by finding the LCM of the denominators.
Which of the following is not a common denominator of 1, $\frac{1}{3}$, and $\frac{1}{4}$?
LCD(1, $\frac{1}{3}, \frac{1}{4}$) = LCM(1, 3, 4) = 12
So, the common denominators are 12, 24, 36, 48, …
Frequently Asked Questions about Common Denominator
What are the fractions with common denominators called?
The fractions with the common denominators are called the like fractions. For example: $\frac{2}{5}$ and $\frac{4}{5}$.
Can common denominators be negative?
No, the common denominators cannot be negative as it represents the common multiples of the denominators, which cannot be negative.
How is LCD different from the common denominator?
Least Common Denominator is the smallest number that can be a common denominator of a set of fractions. On the other hand, the common denominator is the common multiple of the denominators. For example: For the fractions $\frac{3}{5}$ and $\frac{2}{7}$, the least common denominator is 35. The common denominator can be 35, 70, 105, etc.




































